Turing test facts for kids
The Turing test is a clever way to check if a computer can act so much like a human that you can't tell the difference. Alan Turing, a brilliant scientist, came up with this idea. He believed that if a computer could trick a person into thinking it was another human, then that computer must be truly smart.
How the Test Works
The Setup
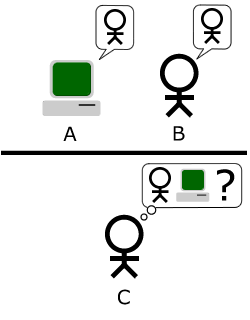
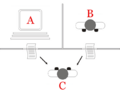
In the Turing test, a person, called the "interrogator," sits in one room. They use a keyboard and screen, like a simple chat program, to talk to two other "players" in different rooms. One of these players is a real human, and the other is a machine (a computer program).
The interrogator's job is to ask questions and have conversations with both players. They can ask anything they want! The goal is to figure out which player is the computer and which is the human.
Passing the Test
If the interrogator cannot tell the difference between the human and the computer more than half the time, then the computer is said to have passed the Turing test. This means the computer is considered "intelligent" because it can fool a human into thinking it's also human.
A Closer Look
Over time, people thought more about the test. They realized that no single human knows everything. So, they suggested that both the human and the computer in the test should be experts in a specific area of knowledge. The interrogator would also be an expert in that same area. This makes the test fairer and more focused.
As of 2009, no computer has fully passed the Turing test. However, some programs have come close. For example, a program named Elbot managed to fool about 30% of the people who tested it.
Images for kids
See also
In Spanish: Prueba de Turing para niños
 | Selma Burke |
 | Pauline Powell Burns |
 | Frederick J. Brown |
 | Robert Blackburn |