Caesar cipher facts for kids

The Caesar cipher is a special way to hide messages. It's a type of cryptography, which is the study of secret codes. This code is named after Julius Caesar, a famous Roman general. He used it to send secret messages to his army so enemies couldn't understand them.
Contents
How the Caesar Cipher Works
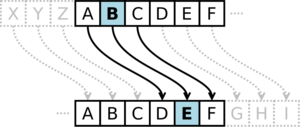
To make a message secret with the Caesar cipher, you change each letter using a simple rule. Julius Caesar's rule was to "shift by three." This means each letter is replaced by the letter three places ahead in the alphabet.
For example:
- A becomes D
- B becomes E
- C becomes F
This continues through the alphabet. When you get to the end, you "wrap around" to the beginning.
- W becomes Z
- X becomes A
- Y becomes B
- Z becomes C
To change the secret message back to normal, you do the opposite. Each letter is replaced by the one three places before it.
Shifting by Different Numbers
While Julius Caesar used a shift of three, the same idea works for any number. You could shift by one, five, or even twenty letters! Each different shift creates a new secret code.
A modern version of this code is called ROT13. It shifts letters by 13 places. This code is often used online to hide spoilers or jokes, but it's very easy to figure out.
Is the Caesar Cipher Safe?
The Caesar cipher is a substitution cipher. This means each letter in the original message is simply replaced by another letter. While it might seem clever, the Caesar cipher is not very safe for truly secret messages.
It's actually quite easy to "break" or decode a Caesar cipher. You can even do it using simple tools like Microsoft Excel or by just trying out all 25 possible shifts. Because of this, much more complex codes are used today to keep information truly secret.
Images for kids
-
The Caesar cipher is named for Julius Caesar, who used an alphabet where decrypting would shift three letters to the left.
See also
 In Spanish: Cifrado César para niños
In Spanish: Cifrado César para niños
 | Anna J. Cooper |
 | Mary McLeod Bethune |
 | Lillie Mae Bradford |