Carex eburnea facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Carex eburnea |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Monocots |
| Clade: | Commelinids |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Cyperaceae |
| Genus: | Carex |
| Subgenus: | Carex subg. Carex |
| Section: | Carex sect. Albae |
| Species: |
C. eburnea
|
| Binomial name | |
| Carex eburnea Boott
|
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
Carex eburnea, also called ivory sedge, ebony sedge, or bristleleaf sedge, is a small, thin plant. It is a type of sedge, which looks a bit like grass. This plant grows naturally across a large part of North America. You can find it from Alaska and Newfoundland all the way south to central Mexico.
About Ivory Sedge
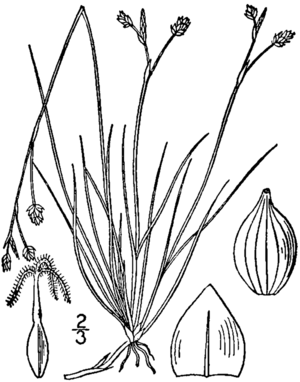
Ivory sedge grows in clumps. It slowly spreads using thin, light brown rhizomes. These are like underground stems that help the plant form new groups.
The plant has narrow leaves, about 0.2 to 1 millimeter wide. They can be 3 to 21 centimeters long. These leaves grow from the bottom of the plant. They also grow one after another along the plant's stems. The stems are longer than the leaves, reaching 7 to 31 centimeters in length.
The bottom parts of the leaves and stems are wrapped in a light brown cover. After the growing season, the leaves dry up. They stay on the plant until at least the next spring.
Flowers and Seeds
Each plant stem has a group of flowers called an inflorescence. At the top of this group is one male flower cluster, called a spike. Below it are two to three female flower clusters. Each female spike is covered at its base by a tube-like leaf called a bract.
Each female spike has 3 to 10 small flowers, called florets. The tiny scales under these florets are white and see-through.
After the flowers are pollinated, they make seeds. These seeds are three-sided and glossy blackish-brown when they are ready. They are about 1.5 to 2.2 millimeters long and 0.7 to 1.1 millimeters wide.
When the plant first blooms, the stems holding the flower clusters are very short. But they grow much longer as the seeds ripen. This makes the seed clusters stand taller than the withered male spike. The main stem of the plant is always longer than its leaves.
Where Ivory Sedge Grows
Ivory sedge usually grows in forests with coniferous trees (like pine or spruce). It can also be found in forests with a mix of tree types. Sometimes, it grows in wet, grassy areas called fens. You might also see it on stable sand dunes or in areas called alvar. Alvar is where there is thin soil over limestone rock.
This plant likes soil that is sandy or gravelly. It prefers soil that is not too acidic, but more neutral to alkaline.