Clinotarsus alticola facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Clinotarsus alticola |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Synonyms | |
|
The Clinotarsus alticola is a type of frog that belongs to the Ranidae family. It has many common names, like the Assam Hills frog, Annandale's frog, pointed-headed frog, and high-altitude frog. This frog lives in the hills of northeastern India, including Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Tripura, and West Bengal. You can also find it in northern Bangladesh, and possibly in Bhutan and Nepal.
Where the Assam Hills Frog Lives
The Clinotarsus alticola frog makes its home in evergreen forests. These forests are usually found in hilly areas. These frogs like to live near large streams, especially close to waterfalls. This is because their tadpoles need these streams to grow.
What the Assam Hills Frog Looks Like
These frogs show something called sexual dimorphism. This means that males and females look a bit different. Male frogs are smaller, measuring about 32 to 47 millimeters from snout to vent (the end of their body). Female frogs are larger, measuring about 43 to 61 millimeters.
When male frogs want to attract a mate, they make a sound. Their call sounds like a bird's "chirp." During the breeding season, there are many more males than females. Males will even try to push other males off the backs of females! Outside of the breeding season, it's quite rare to spot an adult Clinotarsus alticola frog.
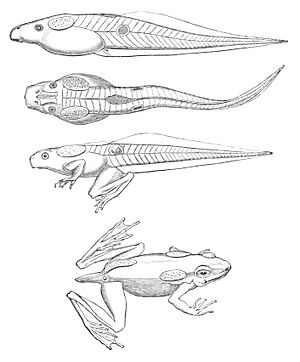
The tadpoles of the Clinotarsus alticola are very special. They are quite large, growing up to 98 millimeters long. They also have many glands on their bodies. These tadpoles are black with red spots, called ocelli. One unique feature is a red spot on their tail, called a caudal ocellus. This is very unusual for frog tadpoles. Their bright colors might be a warning sign to predators, telling them that the tadpoles are not tasty or are even harmful.