Convection heater facts for kids
A convection heater warms a room by moving air around. It uses something called convection to do this. Think of it like a natural air current. Inside the heater, there's a special part called a heating element. This part gets hot.
When air touches the hot heating element, it gets warm. Warm air is lighter than cold air, so it floats up. As the warm air rises, it pushes the cooler air down. This cooler air then gets heated by the element, rises, and the cycle keeps going. This way, the whole room gets warm!
Contents
How Convection Heaters Work
Convection heaters use a simple science trick. When air gets hot, it becomes less dense. This means it's lighter than the cooler air around it. Because it's lighter, the warm air rises.
As the warm air rises, it creates space for cooler air to move in. This cooler air then gets heated by the heater. It rises too, and the cycle continues. This constant movement of air is called a convection current. It helps to spread heat evenly throughout a room.
History of Convection Heating
People have used convection to heat their homes for thousands of years. Early heating systems, like hearths (open fireplaces) and furnaces, mostly worked by heating air and letting it circulate.
Ancient Heating Methods
- 2500 BC: Ancient Greeks used central hearths in their homes. These were like big, fixed fireplaces in the middle of a room.
- 800s AD: Simple fireplaces started to appear.
- 13th Century: Castles in Europe often had fireplaces with basic chimneys. These chimneys helped to pull smoke out of the room.
Modern Heater Developments
Over time, heating technology got better.
- 1713: The first guide on how to design a fireplace was published. It was called Mechanique du Feu.
- 1849: Stoves were invented that could control their own temperature using a thermostat. This was a big step forward!
- 1924: The "Model S" heater was created in Dallas, Texas. It was an early type of convection space heater. This heater pulled in cold air, warmed it up, and pushed it back out. It was very good at heating rooms while staying cool on the outside.
These early ideas, along with new inventions like electricity and better thermostats, led to the modern convection heaters we use today.
Types of Convection Heaters
Convection heaters come in different types, usually based on how they get their power. Some use electricity, while others use gas or other fuels. The part that gets hot (the heating element) can be made of metal coils, special wires, or even ceramic.
Panel Heater
A panel heater is an electric heater. It's often used to warm up a whole room in homes or small offices. People sometimes confuse them with electric radiators. But radiators heat objects directly, while panel heaters warm the air. Panel heaters often have controls for setting the time and temperature. They are usually used to help out a main heating system.
Fan Heater
A fan heater is a mix of a heater and a fan. It blows warm air around a room. The first fan heaters appeared in the 1950s. Modern fan heaters have fans that can change speed. Sometimes, the fan can even work without the heater being on.
Oil Heater
An oil heater is also called a column heater. It uses electricity to heat up oil inside it. This oil doesn't burn; it just gets hot. Oil is good at holding heat and transferring it. So, the hot oil helps to spread warmth from the heating element throughout the heater. This makes the heater warm up the air around it.
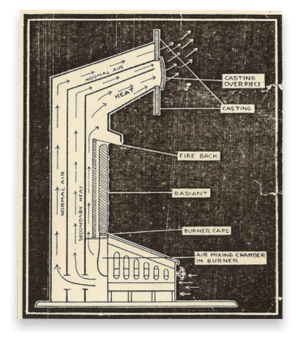
Gas-Fired Convection Heater
A gas-fired convection heater uses gas instead of electricity. These heaters have a gas burner that heats the air. They also have an air filter, gas valves, a blower (like a fan), and a thermostat to control the temperature.