Broad-leaved bloodwood facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Broad-leaved bloodwood |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Corymbia foelscheana at Katherine | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Myrtales |
| Family: | Myrtaceae |
| Genus: | Corymbia |
| Species: |
C. foelscheana
|
| Binomial name | |
| Corymbia foelscheana (F.Muell.) K.D.Hill & L.A.S.Johnson
|
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
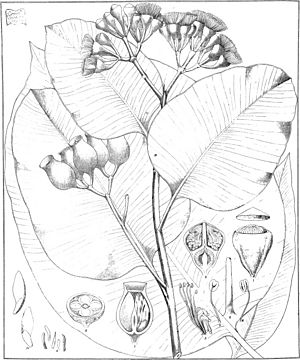
The Corymbia foelscheana, often called the broad-leaved bloodwood, is a small tree. It is also known as the fan-leaved bloodwood or smooth-barked bloodwood. This tree grows only in northern Australia. It has rough, thin bark on its trunk. The bark looks like small, flat pieces fitted together. Higher up, the bark is smooth. Its adult leaves are shaped like wide eggs or spears. The tree usually has groups of seven flower buds. Its flowers are creamy white, and its fruit looks like an urn.
Contents
What Does the Broad-leaved Bloodwood Look Like?
The Corymbia foelscheana is a tree that usually grows to be about 5 to 12 meters (16 to 39 feet) tall. It has a special woody swelling at its base called a lignotuber. This helps the tree regrow after a fire.
Bark and Leaves
The bark on its trunk is thin and rough. It can be brown, grey, or reddish. It peels off in small, flat, puzzle-piece-like flakes. The bark higher up on the tree is smooth and can be white or cream-colored.
Young plants and new shoots have dull green leaves. These leaves are wide and egg-shaped or oblong. They are about 17 to 25 centimeters (7 to 10 inches) long and 15 to 18.5 centimeters (6 to 7 inches) wide. Their edges are often wavy.
Adult leaves grow in an alternating pattern along the branches. They are dull green on both sides. These leaves are broadly egg-shaped to spear-shaped. They measure about 10 to 27.5 centimeters (4 to 11 inches) long and 4 to 13.5 centimeters (2 to 5 inches) wide. Each leaf has a stalk called a petiole, which is about 1.8 to 4 centimeters (0.7 to 1.6 inches) long.
Flowers and Fruit
The tree's flower buds mostly grow at the ends of its branches. They are found on a branched stalk called a peduncle, which is 0.9 to 5 centimeters (0.4 to 2 inches) long. Each branch of the peduncle usually holds seven buds. These buds sit on smaller stalks called pedicels, which are 0.5 to 1.4 centimeters (0.2 to 0.6 inches) long.
Mature buds are oval or pear-shaped. They are about 0.9 to 1.4 centimeters (0.4 to 0.6 inches) long and 0.7 to 0.9 centimeters (0.3 to 0.4 inches) wide. The top part of the bud, called the operculum, is rounded. Sometimes it has a small knob in the center.
This tree blooms from December to January or from January to May. Its flowers are creamy white. After flowering, the tree produces woody, urn-shaped fruit. This fruit is a capsule about 2.2 to 3 centimeters (0.9 to 1.2 inches) long and 1.4 to 2.4 centimeters (0.6 to 0.9 inches) wide. The parts that release the seeds are hidden inside the fruit.
How Did the Broad-leaved Bloodwood Get Its Name?
The broad-leaved bloodwood was first officially described in 1882. A botanist named Ferdinand von Mueller gave it the name Eucalyptus foelscheana. He wrote about it in a publication called The Chemist and Druggist with Australasian Supplement.
The first samples of the tree, known as "type specimens," were collected near Port Darwin. They were found by Paul Foelsche. Later, in 1995, two other botanists, Ken Hill and Lawrie Johnson, changed its name to Corymbia foelscheana.
Where Does the Broad-leaved Bloodwood Grow?
This type of eucalypt tree is found in specific areas. It grows on gentle slopes and low rocky hills. You can find it in open forests and low open woodlands. It prefers loamy soils and laterite soils, which are rich in iron.
The tree grows across northern Australia. Its range stretches from the Kimberley region in Western Australia. From there, it goes east through the "top end" of the Northern Territory. This includes Melville Island.
In these woodland areas, the broad-leaved bloodwood often grows alongside other plants. Some common trees it shares its home with include Erythrophleum chlorostachys and Xanthostemon paradoxus. In the less dense undergrowth, you might see plants like Grevillea decurrens and Gardenia megasperma.
 | Kyle Baker |
 | Joseph Yoakum |
 | Laura Wheeler Waring |
 | Henry Ossawa Tanner |