Critical path method facts for kids
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a way to plan and manage projects. It helps you figure out the quickest way to finish a project by looking at all the tasks involved. CPM is often used with another method called PERT.
Imagine you have a big school project with many steps. CPM helps you list all the steps, how long each takes, and which steps depend on others. Then, it finds the "critical path" – the longest series of tasks that must be done in order a specific way. If any task on this path is delayed, the whole project will be delayed.
Contents
How It Started
The Critical Path Method was created in the late 1950s. Two people, Morgan R. Walker from DuPont and James E. Kelley Jr. from Remington Rand, came up with it. They wanted a better way to schedule complex projects.
Around the same time, another similar method called PERT was developed by the U.S. Navy. The idea of finding a "critical path" was also used in big projects like building the Manhattan Project even earlier, in the 1940s.
Today, CPM is used for all kinds of projects. This includes building things like the World Trade Center Twin Towers (where it was first used in 1966), developing software, doing research, and even maintaining factories. Any project where tasks depend on each other can use this method.
Basic Steps
To use CPM, you need to create a model of your project. This model includes:
- A list of all the tasks needed to finish the project.
- How long each task will take to complete.
- Which tasks must be finished before others can start (their dependencies).
- Important checkpoints or final products (like milestones).
Using this information, CPM calculates the longest path of tasks from start to finish. This path is the "critical path." It also figures out the earliest and latest times each task can start and finish without making the project longer.
Tasks on the critical path are super important. If they are delayed, the whole project gets delayed. Other tasks might have "total float," which means they can be delayed a bit without affecting the project's end date.
For example, if you're testing a solar panel and need to wait for "sunrise," that waiting time might add "float" to tasks before it. This float is part of the shortest possible time for the project.
A project can have several critical paths or paths that are almost critical. Tasks not on the critical path are called "subcritical" or "noncritical." They don't delay the project.
Seeing the Schedule
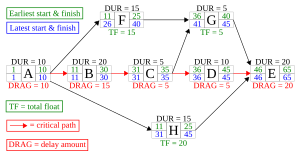
Project managers often use diagrams to see the critical path. One common type is an "activity-on-node" diagram. In this diagram, each task is a box, and arrows show how tasks connect.
In the diagram above, tasks A, B, C, D, and E are on the critical path. Tasks F, G, and H are not. They have extra time (float) of 15, 5, and 20 days. Tasks on the critical path usually cause delays if they take longer. This delay is called "critical path drag."
Knowing the drag helps managers decide which tasks to focus on. They can try to shorten the project by:
- Making critical path tasks shorter.
- Doing more tasks at the same time ("fast tracking").
- Adding more resources (like people or equipment) to critical tasks ("crashing the critical path").
Speeding Things Up
"Crash duration" means the shortest possible time a task can be done. You can achieve this by putting more resources into that task. However, this often costs more money and might even lower the quality of the work because the focus is on speed.
How CPM Adapts
CPM was first just about the order of tasks. But now, it also includes resources like people or equipment. This means it can help manage when resources are available.
Project schedules often change. CPM helps managers keep an eye on the schedule. It warns them if non-critical tasks are delayed too much, which could create a new critical path and delay the project.
Many software programs today use the CPM method to help manage projects.
Staying Flexible
A schedule made with CPM isn't always perfect because it relies on estimates. If an estimate is wrong, the whole plan might change. It's important for project managers to react quickly to these changes. CPM helps by showing how much a change affects the overall schedule. After a project is done, managers can look back at the "as-built critical path" to see what actually happened and why.
See also

- Gantt chart
- Program evaluation and review technique
- Project management
- Project planning
- Work breakdown structure
 | Misty Copeland |
 | Raven Wilkinson |
 | Debra Austin |
 | Aesha Ash |