Cytotoxic T cell facts for kids
A cytotoxic T cell is a special type of white blood cell in your body. Think of it like a tiny, super-smart soldier! Its main job is to find and destroy cells that are sick or dangerous. This includes cancer cells, cells infected with viruses, or cells that are damaged in other ways. These amazing cells are a key part of your immune system, which protects you from illness.
Contents
What are Cytotoxic T Cells?
Cytotoxic T cells are a type of T lymphocyte. They are like the "hitmen" of your immune system. Their main mission is to identify and eliminate cells that could harm your body. This includes cells that have turned into cancer cells or cells that have been taken over by viruses.
How Do T Cells Work?
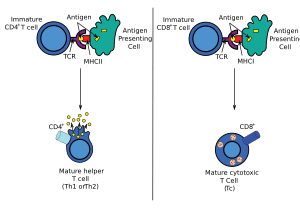
Most cytotoxic T cells have special "antennae" called T-cell receptors (TCRs). Each TCR is designed to recognize a very specific "bad guy" signal, called an antigen. Antigens are like unique ID tags found on the surface of sick or infected cells.
Imagine a cell gets infected by a virus. The infected cell will show tiny pieces of the virus (the antigens) on its surface. It uses special molecules called major histocompatibility complex (MHC) to display these antigens.
When a cytotoxic T cell comes along, its TCR checks these displayed antigens. If the T cell's TCR matches the antigen perfectly, it knows that cell is in trouble. It's like a lock and key!
T Cells: Our Body's Defenders
Once a cytotoxic T cell recognizes a sick or infected cell, it doesn't hesitate. It binds tightly to the target cell. Then, it releases special chemicals that tell the sick cell to self-destruct. This process is very precise. The T cell only destroys the infected or cancerous cell, leaving healthy cells unharmed.
These powerful cells are constantly patrolling your body. They are a vital part of your natural defenses. Without them, your body would struggle to fight off many infections and diseases.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Linfocito T CD8+ para niños
In Spanish: Linfocito T CD8+ para niños