David Easton facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
David Easton
FRSC
|
|
|---|---|
| Born | June 24, 1917 |
| Died | July 19, 2014 (aged 97) |
| Nationality | American |
| Known for | Political systems theory |
David Easton (June 24, 1917 – July 19, 2014) was a very important political scientist. He was born in Canada but became an American citizen. For 50 years, from 1947 to 1997, he taught political science at the University of Chicago.
Easton was a leader in changing how political science was studied. He helped start the "behavioralist" and "post-behavioralist" movements in the 1950s and 1970s. He is famous for defining politics as how society decides who gets what important things. He also used a special way of thinking called "systems theory" to understand how politics works.
Contents
Early Life and Education
David Easton was born in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. He went to the University of Toronto for his first degree, graduating in 1939. Later, he earned his Master's degree in 1943 and his Ph.D. from Harvard University in 1947.
He also received honorary degrees from other universities, like McMaster University. David Easton was married to Sylvia Isobel Victoria Johnstone, and they had one son.
Academic Career and Leadership
Easton began his teaching career at Harvard University from 1944 to 1947. In 1947, he joined the University of Chicago as a professor of political science. He taught there for many years, becoming a highly respected professor.
In 1997, he moved to the University of California, Irvine. There, he helped build a strong graduate program for students studying political science. He taught important courses about the history and foundations of modern political science.
Easton was also a leader in many important organizations. He was the president of the American Political Science Association from 1968 to 1969. This is a major group for political scientists in America. He also served as vice president of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences.
Understanding Politics: Easton's Ideas
David Easton was known for his new ideas about how to study politics. He was one of the first "behavioral revolutionaries" in political science. This means he wanted to make the study of politics more scientific.
The Political System as a Machine
In 1953, Easton wrote a very important book called The Political System. He argued that political science needed better ways to gather and understand information. He wanted to create a "general theory" of politics. This theory would help explain how political events happen and even predict them.
Easton's most famous idea is defining politics as the "authoritative allocation of values for a society." This means politics is about how a society officially decides who gets important things, like resources, rights, or power.
Systems Theory Explained
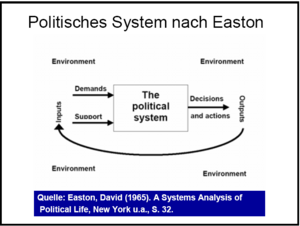
Easton is especially famous for using systems theory to study politics. Imagine politics like a machine or a system. This system has different parts that work together:
- Inputs: These are the things that go into the political system. They include demands from people (like wanting better schools or roads) and support for the government.
- Conversion: This is where the political system processes the inputs. It's where decisions are made, laws are created, and policies are formed.
- Outputs: These are the results or actions that come out of the system. They include new laws, government decisions, or public policies.
- Feedback: This is how the outputs affect the inputs. For example, if a new law is unpopular, people might demand changes, creating new inputs for the system.
- Environment: This is everything outside the political system that can influence it, like the economy, culture, or other countries.
This way of thinking helped many political scientists understand how governments respond to their citizens.
Beyond Just Theory
Later, Easton led another change called the "post-behavioralist revolution." He believed that political science research should not just be about theories. It should also be useful and help solve real-world problems. He thought political scientists should focus on important issues facing society.
This idea helped create the field of public policy studies. It encouraged political scientists to use their knowledge to make society better.
Key Publications
David Easton wrote many influential books and articles. Some of his most well-known works include:
- 1953, The Political System. An Inquiry into the State of Political Science
- 1965, A Framework for Political Analysis
- 1965, A Systems Analysis of Political Life
- 1969, Children in the Political System - Origins of Political Legitimacy (with Jack Dennis)
See also
 In Spanish: David Easton para niños
In Spanish: David Easton para niños