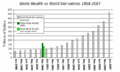
Derivative (finance) facts for kids
A derivative is a special kind of contract or agreement. It's like making a promise today to buy or sell something later, at a price you both agree on right now. This "something" could be many things, like goods (such as oil or corn), money from other countries (like dollars or euros), or even parts of companies (called equities).
People use derivatives for two main reasons. One reason is called speculation. This is when someone hopes the future market price will be different from the price they agreed on in the contract. If they guess right, they can make a profit from the difference.
The second reason is called hedging. This is about protecting yourself. Imagine a farmer who will sell his corn in a few months. He might use a derivative to agree on a price today. This way, he knows exactly how much money he will get, even if the price of corn drops a lot later. For a buyer, hedging means they won't pay more than the agreed price, even if the market price goes up.
One of the oldest examples of derivatives is rice futures. People have been trading these in Japan at the Dojima Rice Exchange since the 1700s. This shows that people have been making these kinds of agreements for a very long time!
Derivatives can come in many forms. Some common types are Futures, Contracts for Difference, and Options. They can be based on different things like foreign exchange (Forex), company shares (Equities), raw materials (Commodities), and even interest rates.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Derivado financiero para niños
In Spanish: Derivado financiero para niños