Developmental psychology facts for kids
Developmental psychology is a cool part of psychology that looks at how people grow and change throughout their lives. It's also called human development. This field studies how our minds and behaviors develop from when we are babies all the way to old age.
Scientists who study developmental psychology are called psychologists. They want to understand how we learn, think, feel, and interact with others as we get older. They study different age groups, like infants, children, teenagers (also called adolescents), and adults.
Developmental psychology explores many areas of human change. This includes how we develop motor skills (like walking or writing), how our problem solving abilities improve, how we understand new ideas, and how we learn language. It also looks at how we develop our moral understanding (what's right and wrong) and our identity (who we are).
Contents
What is Developmental Psychology?
Developmental psychology is all about understanding how people change and grow. Imagine a tiny baby who can only cry and sleep. Then, think about a 15-year-old who can solve complex math problems and play sports. Developmental psychologists study all the steps and changes that happen in between. They look at how our bodies, minds, and feelings develop over time.
Why is it Important to Study Development?
Studying how people develop helps us understand ourselves and others better. It helps parents, teachers, and doctors know what to expect at different ages. For example, knowing how children learn helps teachers create better lessons. Understanding teenage development can help adults support teens through big changes. It also helps us find ways to help people who might be struggling with their development.
Key Areas of Development
Developmental psychologists often focus on different types of changes. These areas are all connected and influence each other.
Physical Development
This area looks at how our bodies grow and change. It includes things like gaining height and weight, developing motor skills (like crawling, walking, running, and fine motor skills like drawing), and changes in our brains. For example, a baby's brain grows incredibly fast in the first few years of life.
Cognitive Development
Cognitive development is about how our thinking skills grow. This includes how we learn, remember, solve problems, and understand the world around us. It's about how our intelligence develops. For instance, a young child might think that if you pour water from a tall, thin glass into a short, wide glass, there's less water. An older child understands that the amount of water stays the same.
Piaget's Theory of Cognitive Development
One very famous psychologist named Jean Piaget studied how children's thinking develops. He believed children go through different stages of thinking as they grow. He showed that children don't just know less than adults; they think in a completely different way. His ideas helped us understand how kids learn about the world.
Social and Emotional Development
This area focuses on how we learn to interact with others and how our feelings develop. It includes learning about friendships, family relationships, and understanding our own emotions. It also covers how we develop our personality and identity. For example, a toddler might have temper tantrums, but an older child learns to manage their feelings better.
Forming Relationships
From birth, babies start to form bonds with their caregivers. This is called attachment. As we grow, we learn how to make friends, work in groups, and understand social rules. These social skills are very important for our well-being.
Understanding Emotions
Learning to recognize and manage our emotions is a big part of development. This includes understanding what makes us happy, sad, angry, or scared, and how to express these feelings in healthy ways.
How Developmental Psychologists Study People
Developmental psychologists use many different ways to study how people change.
Observing Behavior
One common way is to simply watch people. Psychologists might observe how children play together, how babies react to new toys, or how teenagers interact with their friends. This can happen in natural settings, like a playground, or in a special lab.
Experiments
Sometimes, psychologists set up special activities or "experiments" to see how people respond. For example, they might give children a puzzle to solve to see their problem-solving skills. They use careful methods to make sure their studies are fair and accurate.
Surveys and Interviews
For older children, teens, and adults, psychologists might ask questions through surveys or interviews. This helps them understand people's thoughts, feelings, and experiences directly.
Influences on Development
Many things can influence how a person develops.
Nature vs. Nurture
A big question in developmental psychology is "nature versus nurture."
- Nature refers to the things we are born with, like our genes. These are traits passed down from our parents.
- Nurture refers to everything in our environment that influences us, like our family, friends, school, and culture.
Psychologists believe that both nature and nurture play a huge role in shaping who we become.
Family and Culture
Our family is usually the first and most important influence on our development. The way our parents raise us, the values they teach, and the experiences we have at home all shape us. Our culture, which includes our traditions, beliefs, and social rules, also has a big impact on how we develop.
Schools and Peers
As we grow, schools become very important for learning and social development. Our friends, or "peers," also play a big role, especially during the teenage years. We learn a lot from interacting with people our own age.
Famous Developmental Psychologists
Many smart people have contributed to our understanding of human development.
Charles Darwin
While not a psychologist, Charles Darwin (famous for his theory of evolution) also studied his own children's development. He made detailed notes about their behaviors and emotions, which helped start the scientific study of child development.
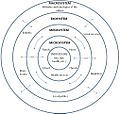
Urie Bronfenbrenner
Urie Bronfenbrenner developed a theory called the "ecological systems theory." He believed that a child's development is influenced by many different layers of their environment, from their immediate family to their wider community and culture. He showed how everything around a child affects their growth.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Psicología del desarrollo para niños
In Spanish: Psicología del desarrollo para niños
 | Emma Amos |
 | Edward Mitchell Bannister |
 | Larry D. Alexander |
 | Ernie Barnes |