Dither facts for kids
Dithering is a clever trick used in digital images and sounds. Imagine you have only a few colors or sound levels to work with, but you want to show many more. Dithering helps by adding a little bit of "noise" or random patterns. This noise helps to spread out errors that happen when you try to simplify colors or sounds. It makes things look smoother and more natural, preventing ugly blocks of color or sudden changes.
Dithering is often used when you convert a colorful image to one with fewer colors, like turning a photo into a black and white picture. It makes sure that the new image still looks a lot like the original, even with fewer details. You'll find dithering used in digital audio and video too, especially when preparing music for a CD.
How Dithering Works with Images
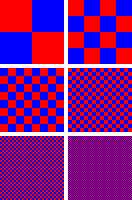
In computer graphics, dithering creates the feeling of having more colors than are actually available. This is super useful when an image has a limited set of colors, also called a "color palette." Instead of just picking the closest color, dithering spreads out different colored pixels from the available palette.
Your eyes are amazing! They blend these tiny dots together. So, even if an image only uses red and blue dots, your eyes might see purple if the dots are small enough and mixed well.
Sometimes, dithered images can look a bit grainy or speckled, especially if you look closely. This is because of the patterns dithering creates. However, if you view the image from a normal distance, your eyes usually blend the dots, and the patterns become less noticeable. Scientists have found that a special kind of pattern called "blue noise" dithering looks the best and is the least distracting.
Dithering Examples
When you reduce the number of colors in an image, it can sometimes lose a lot of detail. For example, a photo might have millions of different colors. If you try to show that photo with only a few hundred colors, some information will be lost.
Let's look at some examples:
- Figure 1 is the original photo. It has many smooth colors.
- Figure 2 shows the same photo, but with fewer colors and no dithering. Notice how some areas look flat or have harsh lines. This is called "color banding."
- Figure 3 uses the same limited colors as Figure 2, but with dithering. See how much smoother and more like the original it looks? Dithering helps get rid of those flat areas and color bands.
Sometimes, the colors chosen for the limited palette are not the best for the image. An "optimized color palette" picks the colors that are most used in the original picture. This often makes the dithered image look even better, as shown in Figure 4.
If you have very few colors, like only 16, the image can lose even more detail. Figure 5 shows an image with only 16 colors and no dithering. The colors look dull, and the banding is very clear. But in Figure 6, with the same 16 colors, dithering helps to make the image much better and reduce the banding.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Tramado para niños
In Spanish: Tramado para niños
 | William M. Jackson |
 | Juan E. Gilbert |
 | Neil deGrasse Tyson |