Compact disc facts for kids
A Compact Disc (often called a CD) is a type of digital optical disc used for storing information. It was created in 1982 by Philips and Sony.
Originally, CDs were made to store and play music. But soon after, they were also used to store computer data. These were called CD-ROMs. Over time, many other types of CDs were made, like CD-R (for recording once), CD-RW (for recording many times), and VCD (for videos). The first CD player for music, the Sony CDP-101, came out in Japan in October 1982.
Most CDs are about 120 millimetres (4.7 in) wide. They can hold up to 80 minutes of music or about 700 MiB of data. Smaller CDs, called Mini CDs, are 60 to 80 millimetres (2.4 to 3.1 in) wide. They are sometimes used for music singles or for storing small computer programs.
Contents
How CDs Started
The idea for recording digital information on a disc came from an American inventor named James T. Russell. He first applied for a patent in 1966. Later, in the 1980s, Sony and Philips got licenses to use his ideas.
CDs were an improvement on an older technology called LaserDisc. LaserDiscs also used a laser to read information, but CDs could store much more data in a smaller space.
In the late 1970s, Philips and Sony worked separately on their own CD ideas. But in 1979, they decided to team up. Engineers from both companies worked together to design a new digital audio disc. After a year, they created the Red Book standard in 1980. This standard set the rules for how all audio CDs should be made.
The CD Becomes Popular
After CDs were released in 1982, they quickly became very popular. Even though early CD players could cost up to $1,000, over 400,000 were sold in the United States between 1983 and 1984.
By 1988, more CDs were sold in the U.S. than vinyl records. By 1992, CD sales were higher than music cassette tapes. The success of the CD was largely because Philips and Sony worked together. They made sure that any CD would work in any CD player, no matter which company made it. This made it easy for people to buy CDs and players, helping the CD become the main way people listened to music at home.
Philips came up with the name compact disc, similar to their Compact Cassette. Philips also helped with the way CDs were made, using ideas from LaserDisc technology. Sony helped with how CDs fix errors when they are read, which makes the sound quality better.
First CDs and Their Launch
Philips opened a factory in Germany to make CDs. Here are some important firsts for the CD:
- The very first test CD was a recording of a classical music piece by Richard Strauss.
- The first public demonstration was on a TV show in 1981. They played the Bee Gees' album Living Eyes.
- The first commercial CD was made on August 17, 1982. It was a recording of Claudio Arrau playing Chopin waltzes.
- The first popular music CD made at the new factory was The Visitors by ABBA.
- The first 50 CD titles were released in Japan on October 1, 1982.
CD players and discs came to Europe and North America in March 1983. People loved the new audio disc, especially those who enjoyed classical music. They praised how good the sound was and how easy CDs were to handle.
As CD players became cheaper, and with the invention of portable players like the Discman, CDs became popular with rock and pop music fans. One of the first things record companies did was re-release popular old albums on CD. This allowed them to sell special boxed sets with many albums.
The first artist to sell a million CDs was Dire Straits, with their 1985 album Brothers in Arms. David Bowie was the first major artist to have all his albums released on CD in 1985. In 1987, the first four albums by The Beatles were released on CD. By 1988, 400 million CDs were made around the world.
CDs Change and Decline
CDs were first made to replace vinyl records for music. But they soon found other uses. In 1985, the CD-ROM (for computer data) was introduced. In 1990, CD-Recordable discs came out. These allowed people to record their own music or copy albums without losing quality.
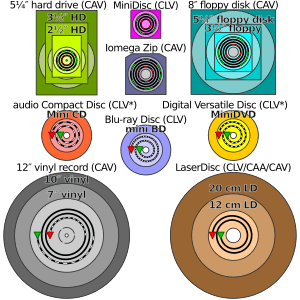
Newer video disc formats like DVD and Blu-ray use a similar shape to CDs. Most DVD and Blu-ray players can still play audio CDs.
By the early 2000s, CD players were common in cars, replacing cassette players. However, with the rise of portable digital music players like mobile phones, CD players are now being removed from cars. Instead, cars have ways to connect phones, like USB or Bluetooth.
Around the same time, music downloads (like MP3s) became very popular on the internet. This caused CD sales to drop a lot in the 2000s. For example, between 2000 and 2008, major record label CD sales went down by 20%.
By 2012, CDs and DVDs made up only 34% of music sales in the United States. By 2015, only 24% of music in the U.S. was bought on physical discs, with CDs being two-thirds of that. However, in Japan in 2015, over 80% of music was still bought on CDs and other physical formats.
Even though sales have dropped, CDs are still found in many places like pharmacies and supermarkets.
How a CD is Made and Works
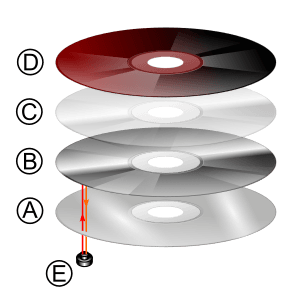
A CD is made from a 1.2 millimetres (0.047 in) thick piece of polycarbonate plastic. It usually weighs between 15 and 20 grams.
The disc has several layers:
- The main part is the plastic disc, where the data is stored as tiny bumps.
- A very thin, shiny layer (usually aluminium or sometimes gold) is put on top. This layer reflects the laser beam.
- A layer of clear lacquer protects the shiny metal.
- The disc's label or artwork is printed on top of the lacquer.
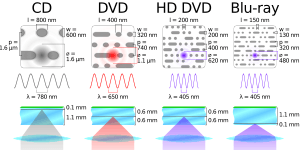
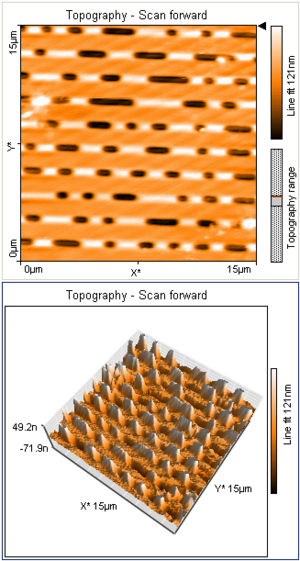
The data on a CD is stored as tiny bumps called "pits" and flat areas called "lands." These are arranged in a long spiral track. Each pit is very small, about 100 nanometers deep and 500 nanometers wide. The tracks are very close together, only 1.6 micrometers apart.
When you play a CD, a motor inside the CD player spins the disc. The speed changes from about 500 rotations per minute (RPM) at the start of the disc to about 200 RPM at the end.
A CD player reads the disc using a semiconductor laser. This laser shines a beam through the bottom of the plastic disc. When the laser hits a pit or a land, the light reflects differently. A sensor called a photodiode measures these changes in light. This allows the player to read the data from the disc. The laser moves on a special arm to read the spiral track from the center to the edge of the disc.
CD Damage
CDs can get damaged from handling or the environment. The data pits are closer to the label side of the disc. This means that scratches on the label side can cause more problems than scratches on the clear side. Scratches on the clear side can sometimes be fixed by polishing them. Sometimes, the edges of CDs are not fully sealed. This can let air or liquids get in and damage the shiny metal layer, making the CD unreadable.
CD Sizes
The digital data on a CD starts in the middle and goes outwards. This design allows for different disc sizes.
- The most common CD size is 120 millimetres (4.7 in) wide. These can hold 74 to 80 minutes of music or 650 to 700 MiB of data. It's a popular story that this size was chosen to fit all of Beethoven's Ninth Symphony on one disc. However, this is a myth!
- Smaller CDs, called "Mini CDs," are 80 mm wide. They can hold up to 24 minutes of music or 210 MiB of data.
Making CDs in Factories
CDs that you buy in stores are made in large factories using a special press. 1. Small plastic pieces are heated and pushed into a mold. 2. The mold closes with a metal stamper that has the CD's data pattern. 3. The plastic cools and hardens, forming the clear plastic disc with the pits and lands. This takes only a few seconds. 4. A thin layer of reflective metal (usually aluminium) is put on the disc. 5. A protective layer of lacquer is added and dried with UV light. 6. Finally, the label is printed on the disc.
To make the metal stamper, a "glass master" disc is first created using a powerful laser. This glass master has the exact pattern of pits and lands. Then, the glass master is used to make the metal stampers that will be used in the presses.
After the CDs are made, they are often wrapped in plastic before being sold in stores.
The most expensive part of a CD used to be its plastic case, called a jewel case. In 1995, the case cost about 30 cents, while the CD itself cost only 10 to 15 cents to make. Even though CDs were cheaper to make than older music formats, they were sold for a higher price because they seemed more valuable. This changed when companies like Apple started selling digital music (MP3s) for a very low price.
Related pages
| Physical size | Audio Capacity | CD-ROM Data Capacity | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 120 mm | 74–80 min | 650–700 MiB | Standard size |
| 80 mm | 21–24 min | 185–210 MiB | Mini-CD size |
| 80x54 mm – 80x64 mm | ~6 min | 10-65 MiB | "Business card" size |
Images for kids
-
The pits in a CD are 500 nm wide, between 830 nm and 3,000 nm long and 150 nm deep.
-
700 MiB CD-R next to a mechanical pencil for scale
See also
 In Spanish: Disco compacto para niños
In Spanish: Disco compacto para niños