CD-R facts for kids
A CD-R (which stands for Compact Disc Recordable) is a special type of compact disc that you can record information onto just once. Think of it like a blank notebook where you can write down notes, but once you write something, you can't erase it and write something new in that spot. People use CD-Rs to save things like music or computer files.
If you need a disc that you can record on many times and erase, you would use a CD-RW instead.
What is "Burning" a CD-R?
When you put data onto a CD-R, it's often called burning the disc. This is because a special tool called a laser uses heat to make tiny marks, called "pits," in a layer of dye inside the disc. These pits become clear, allowing the laser in a CD player or computer drive to read them later as music or data.
What Are CD-R Dyes Made Of?
CD-R discs use different types of special dyes to store information. The color of the dye can often tell you what kind it is:
- Phthalocyanine: This is a very common dye and usually looks light green.
- Cyanine: This dye is often found in discs made by companies like CMC Pro (formerly Taiyo Yuden). It's usually teal or dark green. Older cyanine discs sometimes had problems and could stop working after a few years, but newer ones have special ingredients to prevent this.
- AZO: Verbatim, another disc company, uses AZO dye on some of its discs. This dye is typically dark blue or a blue-ish silver color.
The shiny layer on top of the dye, which helps the laser read the data, is usually made of silver. Some very special discs, like those used for archiving important information or professional audio, might use a gold layer instead. Gold is more stable and lasts longer. For example, Verbatim UltraLife discs have a silver main layer for good reflection and a gold protective layer on top to keep them safe for a long time.
Images for kids
-
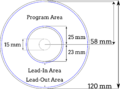
This graphic demonstrates some of the visible features of a CD-R, including the lead-in, program area, and lead-out. A microscopic spiral of digital information begins near the disc's center and progresses toward the edge. The end of the data region and the lead-out can actually be anywhere, depending on how much data is recorded. Data-free areas of the disc and silent portions of the spiral reflect light differently, sometimes allowing track boundaries to be seen
See also
 In Spanish: CD-R para niños
In Spanish: CD-R para niños