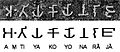Edicts of Ashoka facts for kids
The Edicts of Ashoka are a special collection of 33 messages carved into stone. You can find them on tall stone pillars, large rocks, and even inside cave walls. These messages were made by Emperor Ashoka, who ruled the Mauryan kingdom from 272 to 231 BCE. The edicts tell us a lot about how Buddhism first spread widely across many lands.
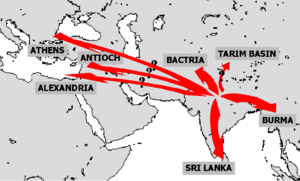
According to these stone messages, Buddhist ideas reached as far as the Mediterranean Sea during Ashoka's time. Many important Buddhist buildings and monuments were also created then.
Emperor Ashoka did not completely stop people from killing animals. However, he wanted people to be careful about how many animals they killed for food. He also made sure some animals were protected and generally said that hurting animals was wrong.
Contents
What Were Ashoka's Stone Messages?
The Edicts of Ashoka are like ancient public announcements. They were carved into stone so everyone could see and read them. Ashoka wanted to share his ideas about a peaceful way of life called Dharma. These messages were placed in many different parts of his large empire.
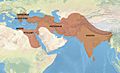
Ashoka's empire was huge, covering much of ancient India. By carving his messages in stone, he made sure his ideas reached many people. These edicts are very important because they are some of the oldest writings from India that we can still read today. They tell us a lot about Ashoka's beliefs and how he wanted his people to live.
Spreading Buddhist Ideas
One of the main goals of Ashoka's edicts was to spread the teachings of Buddhism. After a terrible war, Ashoka felt very sad and decided to follow the path of peace taught by the Buddha. He wanted to share these peaceful ideas with everyone.
The edicts explain that Ashoka sent people to different countries to share Buddhist teachings. These messengers traveled far, even to places like the Middle East and parts of Europe. This shows how widely Buddhism began to spread during Ashoka's rule. He believed that spreading kindness and understanding was a much better way to conquer lands than through war.
Ashoka's Views on Animals
Ashoka cared a lot about all living things. His edicts show his compassion for animals. He didn't ban killing animals completely, but he encouraged people to kill fewer animals for food. He also protected certain animals, like specific types of fish and birds.
He believed that all living beings deserved respect. This was a very new idea for a powerful ruler at that time. Ashoka's messages against violence towards animals were an important part of his Dharma. He wanted his people to live in a way that caused less harm to others, including animals.
Images for kids
-
Brahmi script letters and how they changed over time to modern Devanagari.
See also
 In Spanish: Edictos de Ashoka para niños
In Spanish: Edictos de Ashoka para niños