Electric fish facts for kids

An electric fish is a special kind of fish that can create its own electric fields. Fish that can make these fields are called electrogenic. Those that can sense or detect electric fields are called electroreceptive. Most electric fish can both make and sense electric fields.
Many other fish, like sharks, rays, and catfishes, are electroreceptive. This means they can sense electric fields. However, they cannot create their own electric fields. So, they are not considered electric fish. Most bony fish cannot make or sense electric fields at all.
Contents
Strongly and Weakly Electric Fish
Electric fish have a special body part called an electric organ. This organ helps them make electricity. It is usually found near the fish's tail. The electric organ is made from special muscle or nerve cells. When this organ creates and releases electricity, it's called an electric organ discharge (EOD).
Electric fish are grouped into two types based on how strong their EOD is:
Strongly Electric Fish
These fish create very powerful electric shocks. Their EOD is strong enough to stun or capture their prey. They can also use it to defend themselves. Famous examples include the Electric eel (which is a type of knifefish, not a true eel), electric catfishes, and electric rays.
Weakly Electric Fish
The electric discharge from these fish is not strong enough to stun prey. Instead, they use their electricity for other important tasks. They use it to find objects around them, to navigate in dark or murky water, or to talk with other electric fish. Good examples of weakly electric fish are Peters' elephantnose fish and Black ghost knifefish.
There are about 348 known types of electric fish. They belong to about 56 different groups. Most electric fish live in fresh water. The only known types that live in salt water are the electric rays, with 23 different species.
Images for kids
-
Among the electric fishes are electric eels, knifefish capable of generating an electric field, both at low voltage for electrolocation and at high voltage to stun their prey.
-
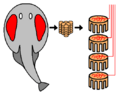
An electric ray (Torpediniformes) showing paired electric organs in the head, and electrocytes stacked within it
See also
 In Spanish: Anguila eléctrica para niños
In Spanish: Anguila eléctrica para niños