Fallopian tube facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Fallopian tube |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
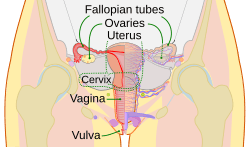
| Schematic frontal view of female anatomy | |
 |
|
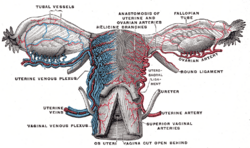
| Vessels of the uterus and its appendages, rear view. (Fallopian tubes visible at top right and top left.) | |
| Latin | tuba uterina |
| Gray's | subject #267 1257 |
| Artery | tubal branches of ovarian artery, tubal branch of uterine artery |
| Lymph | lumbar lymph nodes |
| Precursor | Müllerian duct |
| MeSH | Fallopian+Tubes |
The fallopian tubes (also called oviducts or uterine tubes) are important parts inside a girl's body. They are like tiny, narrow tubes that connect the ovaries to the uterus. Every girl has two Fallopian tubes, one on each side of the uterus.
Contents
What Are Fallopian Tubes?
The Fallopian tubes are about 10 to 13 centimeters (4 to 5 inches) long. They are very thin, about the size of a pencil lead. These tubes are not directly attached to the ovaries. Instead, they have finger-like ends called fimbriae that reach out towards the ovary.
Parts of the Fallopian Tube
Each Fallopian tube has different sections:
- Infundibulum: This is the funnel-shaped part closest to the ovary. It has the fimbriae that help catch the egg.
- Ampulla: This is the widest and longest part of the tube.
- Isthmus: This is a narrow section that connects the ampulla to the uterus.
- Intramural (or interstitial) part: This is the part that passes through the wall of the uterus.
What Do Fallopian Tubes Do?
The main job of the Fallopian tubes is to help an egg travel. Once a month, an egg is released from one of the ovaries. This process is called ovulation. The fimbriae at the end of the Fallopian tube gently sweep over the ovary to pick up the released egg.
Inside the Fallopian tube, there are tiny, hair-like structures called cilia. These cilia, along with muscle movements in the tube, help push the egg slowly towards the uterus. This journey usually takes a few days.
Why Are They Important?
The Fallopian tubes are a key part of the female reproductive system. They provide the path for the egg to move from the ovary to the uterus. Without healthy Fallopian tubes, the egg cannot reach the uterus.
See also
 In Spanish: Trompa uterina para niños
In Spanish: Trompa uterina para niños

