Feynman diagram facts for kids
A Feynman diagram is a special drawing that helps scientists understand what happens when tiny particles crash into each other. Think of it like a map for subatomic particles!
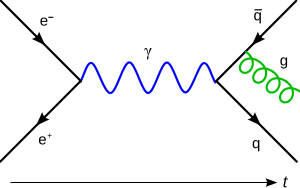
These diagrams are used in a field called quantum mechanics, which studies the smallest things in the universe. A Feynman diagram uses different kinds of lines—like straight, dotted, or squiggly ones. These lines meet at specific spots called vertices.
The lines in a diagram show how a particle moves from one place to another. The vertices are where particles meet, interact, or change. This means two or more particles are at the same spot at the same time.
In these diagrams, particles can even seem to travel backward in time! When a particle goes backward in time, it's actually called an antiparticle. For example, an electron going backward in time is like a positron (its antiparticle) going forward. The meeting points (vertices) can also show particles being created or destroyed. It depends on which way the particle is moving in time.
Contents
Understanding the Diagrams
Every line and vertex in a Feynman diagram has a special number called an amplitude. This number helps scientists figure out the chances of something happening. By multiplying these amplitudes together, they can calculate the total chance for particles to do what the diagram shows.
Scientists add up all these chances for different diagrams. This helps them predict what will happen when particles collide in a machine like a particle accelerator. It tells them the total chance that particles will bounce off each other in a certain way.
Who Created Feynman Diagrams?
Feynman diagrams are named after Richard Feynman. He was a brilliant physicist who won the Nobel Prize in Physics. He made these diagrams much simpler, especially for a theory called quantum electrodynamics (QED).
Feynman Diagrams in QED
In QED, there are only two main types of particles:
- Electrons: These are tiny particles found inside atoms.
- Photons: These are particles of light.
In QED, the only basic thing that can happen is an electron (or its antiparticle) giving off or taking in a photon. So, there's just one main building block for any interaction. The chance of this happening is very simple. It's related to the electron's charge, which is its electrical property.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Diagrama de Feynman para niños
In Spanish: Diagrama de Feynman para niños