Flat huntsman facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Flat huntsman |
|
|---|---|
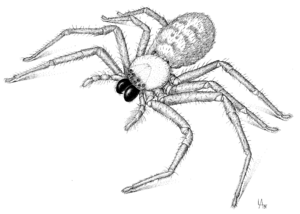 |
|
| Illustration by Des Helmore | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Subphylum: | Chelicerata |
| Class: | Arachnida |
| Order: | Araneae |
| Infraorder: | Araneomorphae |
| Family: | Sparassidae |
| Genus: | Delena |
| Species: |
D. cancerides
|
| Binomial name | |
| Delena cancerides Walckenaer, 1837
|
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The flat huntsman (Delena cancerides) is a large, brown huntsman spider. People also call it the social huntsman or Avondale spider. It is originally from Australia.
This spider was brought to New Zealand in 1924. In New Zealand, it is often called the Avondale spider because it is common in the Avondale area of Auckland. You might have seen this spider in movies like Spider-Man (2002), Napoleon (1995), and Arachnophobia (1990). These movies show the spider as very dangerous. However, in real life, the flat huntsman is usually harmless to humans. Charles Athanase Walckenaer first described this spider in 1837.
Spider Behavior
The flat huntsman spider is quite special because it is a social species. This means they live together in groups, which is unusual for spiders. They even share their food! You can often find them living under loose tree bark. Their flat body shape helps them fit into these tight spaces.
These spiders can form large groups, sometimes with up to 300 spiders in one colony. However, they can be very aggressive towards spiders from other colonies. They might even eat spiders from different groups. Flat huntsman spiders do not spin webs to catch food. Instead, they actively hunt for their prey. They are generally shy around people. If a bite does happen, it usually causes only very minor symptoms.
Where They Live
You can find the flat huntsman spider all over Australia, including Tasmania. It was introduced to New Zealand in 1924. From Avondale, a suburb of Auckland, the spider slowly spread to other parts of New Zealand. This is why it got its New Zealand name, the Avondale spider. There is even a sculpture of this spider in the Avondale shopping center!
Appearance of the Flat Huntsman
Male flat huntsman spiders are about 20 to 25 millimeters (0.8 to 1 inch) long. Females are larger, measuring about 25 to 32 millimeters (1 to 1.3 inches) long. Their bodies are light brown and covered in many fine hairs. Their legs are also hairy and can spread out to more than 15 centimeters (6 inches) wide.
Spiders from different places might look a little different. Scientists have found small differences in their internal makeup depending on where they live. However, even with these small differences, they are still the same species.



