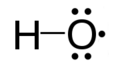Free radical facts for kids
A free radical is a tiny particle, called a molecule, that has a special problem: it has an electron that isn't paired up. Think of it like a single sock looking for its match! Because this electron is all alone, the free radical becomes very active and tries to find another electron to pair with.
When a free radical tries to find its missing electron, it can "steal" one from other healthy molecules in your body. This can cause damage to your cells and lead to different health issues. Things like pollution, cigarette smoke, and even stress can increase the number of free radicals in your body.
Contents
What are Free Radicals?
Free radicals are molecules that are missing one of their electrons. This makes them unstable and very reactive. They are always looking to "steal" an electron from another molecule to become stable. When they do this, they can damage the molecule they stole from.
Imagine a free radical as a hungry little Pac-Man. It zips around, trying to gobble up electrons from other molecules. When it takes an electron, it leaves the other molecule damaged.
Why are Free Radicals a Problem?
When free radicals take electrons from healthy cells, they can cause harm. This damage can be compared to rust forming on metal. Over time, this damage can affect how your body works.
Scientists believe that too many free radicals can contribute to various health problems. They can also play a part in the natural aging process of our bodies.
How Do We Get Free Radicals?
Our bodies naturally make some free radicals as part of everyday processes. For example, when we breathe or exercise, our bodies create them.
However, we can also get free radicals from outside sources. These include:
- Air Pollution
- Cigarette smoke
- Sunlight
- Some foods we eat
- Stress and illness
These external factors can increase the number of free radicals in our bodies.
What Are Antioxidants?
Luckily, our bodies have a defense system against free radicals! This defense comes from things called antioxidants. Antioxidants are like superheroes for your cells.
Antioxidants work by giving an electron to the free radical. This makes the free radical stable and stops it from damaging other cells. They "neutralize" the free radicals.
You can find many antioxidants in healthy foods. Fruits and vegetables are packed with them! Eating a colorful variety of fruits and veggies helps your body fight off free radicals.
Images for kids
-
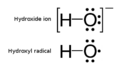
A hydroxide ion compared to a hydroxyl radical.
-
The light from a butane torch showing excited molecular radical bands.
-
Moses Gomberg (1866–1947), who helped start the study of radical chemistry.
See also
 In Spanish: Radical (química) para niños
In Spanish: Radical (química) para niños