Fume hood facts for kids

A common modern fume hood.
|
|
| Other names | Hood Fume cupboard Fume closet |
|---|---|
| Uses | Fume removal Blast/flame shield |
| Related items | Laminar flow cabinet |
A fume hood is a special piece of equipment you often see in chemistry labs. It's like a safety cabinet that protects scientists. Its main job is to keep people safe from dangerous fumes or chemicals. It does this by sucking away bad air and acting as a shield.
Fume hoods are very important for keeping labs safe. They help scientists work with chemicals without getting hurt.
Contents
What is a Fume Hood?
A fume hood is a large, enclosed workspace. It has a big glass window that can be moved up and down. This window is called a sash. Scientists open the sash when they need to put things inside the hood.
Inside, there's a powerful fan. This fan pulls air and any harmful fumes away from the scientist. The air then goes through a special filter or is sent outside. This stops the bad air from spreading in the lab.
Why are Fume Hoods Important?
Fume hoods protect scientists in several ways. First, they remove dangerous gases and vapors. Many chemicals used in labs can create fumes that are not safe to breathe. The fume hood sucks these fumes away.
Second, the glass sash acts like a shield. If a chemical splashes or a small explosion happens, the sash protects the scientist. This means they can work with risky materials more safely. Most chemical reactions that produce fumes or might be dangerous are done inside a fume hood.
How a Fume Hood Works
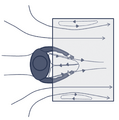
A fume hood works by creating a constant flow of air. Air is pulled in from the front opening. It then moves across the work surface and up into the hood's ventilation system. This system includes ducts and a fan.
The fan pulls the air out of the lab. This creates a negative pressure inside the hood. This means air always flows into the hood, not out into the room. This stops fumes from escaping into the lab where people are working.
Parts of a Fume Hood
- Sash: This is the movable glass window. It protects the user and controls the airflow.
- Work Surface: This is the flat area inside where experiments are done. It's often made of materials that can resist chemicals.
- Blower/Fan: This is the motor that pulls air and fumes out of the hood.
- Ductwork: These are the pipes that carry the air from the hood to the outside or to a filtering system.
- Controls: These are buttons or knobs to turn the fan on or off. Some hoods also have alarms if the airflow isn't strong enough.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Campana de gases para niños
In Spanish: Campana de gases para niños