Genomics facts for kids
Genomics is a super cool science that studies all the genes of an organism. Think of it like looking at the complete instruction book for life, called a genome. This field explores the entire DNA code of living things and how all the genes work together.
Scientists use special tools and computer programs, called bioinformatics, to read, put together, and understand what genomes do. While regular genetics might focus on just one or a few genes, genomics looks at all of them at once. It's like studying every single word in a giant book, instead of just a few sentences!
Contents
What is a Genome?
A genome is the complete set of DNA instructions found in a cell. For humans, our genome contains about 3 billion DNA letters! These instructions tell our bodies how to grow, develop, and function. Every living thing, from tiny bacteria to huge whales, has its own unique genome.
How Genomics Works
Genomics uses amazing technology to read the long strands of DNA. This process is called DNA sequencing. Imagine you have a very long secret message, and DNA sequencing is how scientists decode it letter by letter.
Once the DNA is sequenced, scientists use powerful computers to put all the pieces back together, like solving a giant puzzle. This helps them understand the order of genes and how they might work.
Tools for Genomics
- DNA Sequencing Machines: These are special machines that can read millions of DNA letters very quickly.
- Bioinformatics: This is a field that uses computers and special software to store, organize, and analyze the huge amounts of data from genomes. It helps scientists find patterns and meanings in the DNA code.
Why is Genomics Important?
Genomics is a very important field that helps us understand life in many ways.
Understanding Health and Disease
By studying the human genome, scientists can learn more about diseases like cancer or diabetes. They can find out which genes might make someone more likely to get a certain illness. This can lead to new ways to prevent or treat diseases. For example, doctors might use genomics to choose the best medicine for a patient based on their unique genes.
Improving Agriculture
Genomics helps farmers grow better crops and raise healthier animals. Scientists can use genomics to find genes that make plants resistant to diseases or grow faster. This can help feed more people around the world.
Studying Evolution
Genomics also helps us understand how different species are related and how life has changed over millions of years. By comparing the genomes of different animals or plants, scientists can see how they evolved from common ancestors.
Environmental Science
Scientists use genomics to study tiny organisms in the environment, like bacteria in the soil or ocean. This helps them understand how these organisms affect our planet, from cleaning up pollution to helping plants grow.
History of Genomics
The idea of genomics really took off with the Human Genome Project. This was a huge international effort that started in 1990. Its main goal was to read and map all the genes in the human body.
The Human Genome Project
- Start Date: 1990
- Completion Date: 2003 (most of the genome was sequenced)
- Goal: To find the sequence of all 3 billion DNA letters in the human genome.
- Impact: This project opened up a whole new world for science. It made it much easier and cheaper to sequence DNA, leading to many new discoveries in medicine and biology.
Since the Human Genome Project, the cost of sequencing a genome has dropped a lot. This means more and more scientists can use genomics in their research, leading to exciting new breakthroughs every day!
Images for kids
-
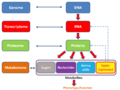
This diagram shows how the genome (all genes), transcriptome (gene messages), proteome (proteins), and metabolome (small molecules) are connected.
See also
 In Spanish: Genómica para niños
In Spanish: Genómica para niños