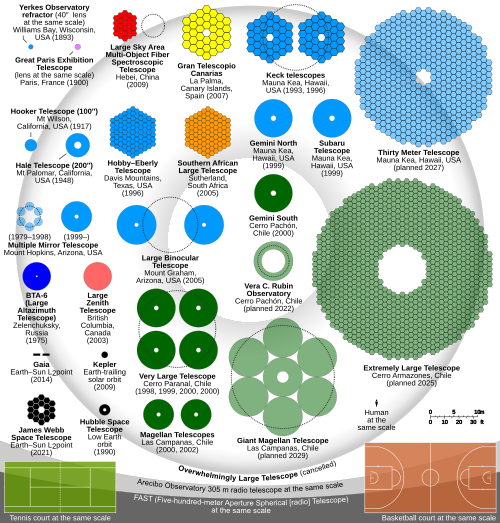
Gran Telescopio Canarias facts for kids
The Gran Telescopio Canarias (or GTC) is a giant telescope in Spain. It's located on La Palma island, part of the Canary Islands. It's the biggest single telescope in the world that uses mirrors to see light.
Building the GTC took seven years and cost a lot of money, about €130 million. It was tricky to build because of bad weather and moving heavy parts to a remote mountain top. The telescope first saw light in 2007, and scientists started using it for research in 2009.
Many groups worked together to build the GTC. These include organizations from Spain and Mexico, plus the University of Florida. Over 1,000 people from 100 companies helped plan and build it. Spain gets to use 90% of the telescope's time, while Mexico and the University of Florida each get 5%.
Contents
History of the GTC
The Gran Telescopio Canarias is a huge and important tool for astronomers. Its journey from an idea to a working observatory involved many steps.
First Look at the Stars
The GTC began its first observations on July 13, 2007. At first, it used 12 special mirror pieces made of a strong glass material called Zerodur. These pieces were made by a German company. Later, the telescope had all 36 of its hexagon-shaped mirror segments installed. These segments work together like one giant mirror, controlled by a smart computer system.
The first tool used with the GTC was called OSIRIS. It helps scientists take pictures and study light from space. Regular scientific observations, where astronomers use the telescope for their research, started in May 2009.
Official Opening Ceremony
The Gran Telescopio Canarias was officially opened on July 24, 2009. King Juan Carlos I of Spain attended the ceremony. More than 500 people, including astronomers, government officials, and journalists, came from different parts of the world to celebrate this big event.
How the GTC Works
The GTC is a reflecting telescope. This means it uses mirrors to collect light from distant objects in space. It has a main mirror that is 10.4 m (410 in) across. This mirror is made of 36 smaller, hexagonal segments that work together perfectly.
The telescope is located at the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory. This spot is high up on a mountain, which is great for stargazing. Being high above the clouds means the air is clearer, and there's less light pollution. This helps the GTC get very clear views of the universe.
Telescope Instruments
The GTC uses special instruments to help astronomers study the light it collects. These instruments allow scientists to do different kinds of research, like taking detailed pictures or breaking down light into its colors to learn about what things in space are made of.
MEGARA
MEGARA is an instrument that helps astronomers study light in a very detailed way. It can look at both visible light and light that's almost infrared. It's like having a super-powered magnifying glass for light.
MEGARA can do two main things:
- It can study a small area of space very closely, like zooming in on a specific part of a galaxy.
- It can also look at up to 92 different objects at the same time across a wider area. This is useful for studying many stars or galaxies at once.
This instrument uses tiny optical fibers, like very thin glass threads, to carry light from the telescope to its sensors.
CanariCam
CanariCam was an instrument that could see in infrared light. This is a type of light that we can't see with our eyes, but we can feel as heat. CanariCam was good at taking pictures and studying the heat coming from objects in space.
It was designed to be very precise and could even block out bright light to see fainter objects nearby. CanariCam worked best in a specific range of infrared light. It was also designed to be compact and didn't need special, hard-to-handle cooling liquids like some older instruments.
CanariCam used a special cooling system to keep its parts and detector very cold, which helped it work efficiently. It was taken out of service in February 2021.
OSIRIS
OSIRIS is another important instrument on the GTC. It helps astronomers take pictures and study light from space. It can see light from ultraviolet to near-infrared.
OSIRIS has a wide view, which is good for taking pictures of large areas of the sky. It can also use special filters to look at very specific colors of light. This helps scientists learn more about the objects they are observing.
See also
 In Spanish: Gran Telescopio Canarias para niños
In Spanish: Gran Telescopio Canarias para niños
- La Silla Observatory
- Mauna Kea Observatories
- Paranal Observatory
- Extremely large telescope
- List of largest optical reflecting telescopes
- List of largest optical telescopes historically
Images for kids