Hematopoiesis facts for kids
Hematopoiesis is a fancy word for how your body makes all its blood cells! Imagine a super busy factory inside you, working non-stop. Every single day, your body produces an amazing 100 to 1,000 billion new blood cells. This keeps your blood healthy and working perfectly.
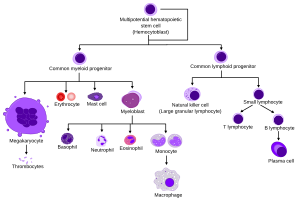
All these different blood cells start from special "master" cells called hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). You can think of them as the original building blocks for all blood cells. These important stem cells live deep inside your bones, in a spongy part called the bone marrow.
As a hematopoietic stem cell grows up, it starts to change. It becomes more specific about what kind of blood cell it will be. This process is called cellular differentiation. It's like a general worker learning to become a specialist, like a carpenter or an electrician. Scientists can often track these changes by looking at special proteins on the outside of the cell. Each step brings the cell closer to its final job, like becoming a red blood cell or a white blood cell.
Studying these amazing stem cells for many years has helped us understand so much about our bodies. Thanks to this research, doctors can now use HSC transplants to help treat serious illnesses like some cancers and problems with the immune system.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
This diagram shows some important signals (called cytokines) that help decide what type of blood cell will be made. SCF= Stem cell factor; Tpo= Thrombopoietin; IL= Interleukin; GM-CSF= Granulocyte Macrophage-colony stimulating factor; Epo= Erythropoietin; M-CSF= Macrophage-colony stimulating factor; G-CSF= Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor; SDF-1= Stromal cell-derived factor-1; FLT-3 ligand= FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 ligand; TNF-a = Tumour necrosis factor-alpha; TGFβ = Transforming growth factor beta