Dilation (geometry) facts for kids
In geometry, dilation is a cool way to change the size of a shape without changing its shape. Think of it like zooming in or out on a picture on your phone! It's a type of transformation, which means moving or changing a shape in some way. When you dilate a figure, the new figure (called the "image") looks exactly like the original, just bigger or smaller. This means they are similar to each other.
Contents
What is Dilation?
Dilation is defined by two main things:
- A special point called the center of dilation. Let's call this point V. It's like the anchor point from which everything grows or shrinks.
- A number called the scale factor. Let's call this number k. This number tells you how much bigger or smaller the new shape will be.
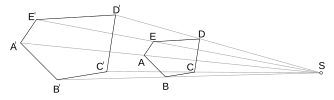
Imagine you have a point P on a shape. When you dilate it, its new position, P' (pronounced "P prime"), will be on the same straight line that connects P to the center of dilation V. The cool part is that the distance from V to P' is exactly k times the distance from V to P.
How Does Dilation Work?
Let's say you have a shape, like a triangle, and you want to dilate it.
- First, you pick your center of dilation (V).
- Then, for each corner (or "vertex") of your triangle, you draw a straight line from V, through that corner.
- Next, you measure the distance from V to that corner.
- You multiply that distance by your scale factor (k).
- You then mark the new point along the line you drew. If k is 2, the new point will be twice as far from V as the original point. If k is 0.5, it will be half as far.
- Do this for all the corners, and then connect your new points to form the dilated shape!
Scale Factor: Making Shapes Bigger or Smaller
The scale factor (k) is super important because it controls the size change:
- If k is greater than 1 (like 2, 3.5, or 10), the new shape will be bigger than the original. It's an enlargement!
- If k is between 0 and 1 (like 0.5, 1/4, or 0.8), the new shape will be smaller than the original. It's a reduction!
- If k is exactly 1, the new shape will be the exact same size as the original. It doesn't change at all!
Dilation in Real Life
You might not realize it, but dilation happens all around us!
- When you use a projector to show a movie or presentation, the image on the screen is a dilation of the image on the projector's lens.
- Photographers use lenses that can zoom in or out, which is a form of optical dilation.
- Architects and engineers use scale drawings and blueprints. These are dilations of the actual buildings or objects they represent.
- Even your eyes perform a type of dilation when they adjust to focus on objects at different distances, changing the size of the image on your retina.