Hydrogel facts for kids
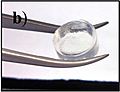
Hydrogels are special materials that are mostly made of water. Think of them like a super-absorbent sponge, but instead of just soaking up water, they hold it inside a special network. This network is made of tiny chains called polymers.
These polymers love water! They can swell up and hold a huge amount of water, sometimes even 90% or 99% of their total weight. Even when they're full of water, hydrogels keep their shape. This is because the polymer chains are linked together, either chemically or physically.
Some hydrogels are linked physically, like a rubber band. You can stretch them and they'll go back to their original shape. Others are linked chemically, which makes them very strong and helps them keep their shape even better. Hydrogels are also a bit like jelly or slime; they can be both liquid-like and solid-like at the same time. This is called being viscoelastic.
Just like other polymers, some hydrogels are found in nature, while others are made by people. The ones made by people are called synthetic hydrogels. These synthetic hydrogels can last longer, hold even more water, and are often stronger than natural ones.
Contents
What are Hydrogels?
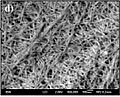
Hydrogels are like tiny, watery sponges made from polymers. Polymers are long chains of repeating small molecules. In hydrogels, these chains are connected to each other, forming a 3D net. This net can trap and hold a lot of water.
How Hydrogels Work
Imagine a fishing net. If you throw it into the water, it can scoop up fish. Hydrogels work a bit like that, but instead of fish, their polymer net scoops up water molecules. The water gets trapped inside the net, making the hydrogel swell up. Even though they hold so much water, they stay solid and don't dissolve. This is thanks to the connections, or cross-links, between the polymer chains. These cross-links are like tiny knots that hold the net together.
Types of Hydrogels
There are many different kinds of hydrogels, and they can react to different things in their environment.
- pH-sensitive hydrogels: These hydrogels change when the pH (how acidic or basic something is) of their surroundings changes. For example, they might swell or shrink.
- Temperature-sensitive hydrogels: These react to how hot or cold it is. They might change their size or stiffness when the temperature goes up or down.
- Electro-sensitive hydrogels: These hydrogels can shrink or expand when an electric field is applied to them.
- Light-responsive hydrogels: These special hydrogels react to light. They might change their shape or properties when light shines on them.
Where are Hydrogels Used?
Hydrogels are very useful because they are so similar to parts of our own bodies. Our bodies are mostly water, and many of our tissues have a watery matrix around cells. This makes hydrogels perfect for many jobs, especially in medicine.
Hydrogels in Medicine
Because hydrogels are full of water and feel like real body tissues, they are great for:
- Tissue engineering: Scientists can use hydrogels to help grow new tissues or repair damaged ones. They can provide a good environment for cells to grow and thrive.
- Delivering medicine: Hydrogels can be designed to hold medicines and release them slowly into the body.
- Wound dressings: Some bandages use hydrogels to keep wounds moist, which helps them heal faster. They are often used for blisters and burns.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Hidrogel para niños
In Spanish: Hidrogel para niños
 | Sharif Bey |
 | Hale Woodruff |
 | Richmond Barthé |
 | Purvis Young |