Information system facts for kids
An information system (or IS) is like a special team that helps organizations handle information. It's designed to gather, work with, save, and share important facts and figures. Think of it as a system that combines people, tasks, rules, and technology to make sure information flows smoothly.
A computer information system is a type of information system that uses computers. It's a team of people and computers working together to process or understand information. Sometimes, this term just means a computer with special programs installed.
"Information systems" is also a field of study. It looks at how computer hardware and software work with people to collect, sort, process, create, and share data. This field focuses on how these systems have clear boundaries, users, ways to process data, storage, inputs, and outputs.
In many companies, the group in charge of information systems is called "information services." Their main goal is to help with daily tasks, manage things, and assist with making good decisions. An information system includes the technology a company uses and how people interact with that technology to get work done.
Some experts see information systems as a special kind of "work system." A work system is where people or machines do tasks using tools to create products or services. An information system is a work system focused on capturing, sending, storing, finding, changing, and showing information.
Information systems are closely linked to data systems and activity systems. They act like a communication system where data is processed as a kind of shared memory. They can also be seen as a way to help people make decisions and take action.
Contents
What is an Information System?
Information systems are made up of several key parts. Experts like Silver et al. (1995) describe them as including software, hardware, data, people, and procedures.
The Association for Computing Machinery says that "Information systems specialists" help businesses by combining technology solutions with business tasks. This helps companies get the information they need.
There are many kinds of information systems. Some examples include systems for handling daily transactions, systems that help with decisions, and systems for managing knowledge. A key part of most information systems is information technology. This technology helps people do things the human brain isn't great at, like handling huge amounts of information or doing complex math.
Information technology is a very important tool for leaders in companies. Many companies have a chief information officer (CIO). This person is a top executive, working alongside the CEO (Chief Executive Officer) and CFO (Chief Financial Officer). The CIO makes sure the company's information systems are working well.
Six Important Parts
To create a working information system, six main parts need to come together:
- Hardware: This means the physical machines and equipment. In today's systems, it includes the computer itself and all its supporting parts. This covers things like keyboards, screens, storage drives, and internet devices. In older systems, hardware might have been ledgers (big books) and pens!
- Software: This refers to computer programs and any instructions that come with them. Programs are like recipes that tell the computer's hardware what to do. They help turn raw data into useful information. Software is usually saved on a disk or tape.
- Data: Data are the raw facts that the system uses to create information. In modern systems, data is stored digitally. In older systems, data was written down by hand. Data is the link between the hardware and the people using the system.
- Procedures: These are the rules and steps that guide how an information system works. Think of them as the instructions for the people using the system, just like software is the instructions for the hardware.
- People: Every system needs people to be useful. This includes the users, those who operate and fix the computers, those who manage the data, and those who support the computer networks. People are often the most important part for an information system to succeed.
- Internet: The internet connects data and people. While not always needed, it's a huge part of many modern systems.
When people interact with data, that data becomes information.
Different Kinds of Systems
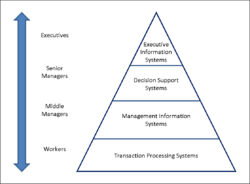
In the past, textbooks often showed information systems as a pyramid. At the bottom were systems for daily tasks, then systems for management, then for decision-making, and at the top, systems for top executives. Even though this pyramid model is still helpful, many new technologies and types of information systems have appeared that don't always fit perfectly into it.
Some examples of these systems include:
- Intelligent systems (like AI)
- Data warehouses (big storage for data)
- Decision support systems (help with choices)
- Enterprise systems (for whole companies)
- Geographic information systems (for maps and locations)
- Management information systems (for managing)
- Search engines (like Google)
- Office automation (tools for office work)
A computer-based information system uses computer technology for some or all of its tasks. Its main parts are:
- Hardware: Devices like monitors, processors, printers, and keyboards. They work together to take in, process, and show data.
- Software: The programs that let the hardware process data.
- Databases: Collections of related files or tables that hold data.
- Networks: Systems that connect different computers so they can share resources.
- Procedures: The instructions for combining all these parts to process information and get the desired results.
The first four parts (hardware, software, databases, and networks) form what's called the information technology platform. People who work in IT use these parts to create systems that help with safety, risks, and managing data. These are called information technology services.
Some information systems help specific parts of a company, while others support the whole organization. For example, each department might have its own systems, like accounting systems, finance systems, or marketing systems. These are called functional area information systems (FAIS). They support bigger systems like business intelligence systems.
Other types of organizational information systems include systems for daily transactions, enterprise resource planning (ERP), and electronic commerce systems. Dashboards are special systems that give all managers quick access to important information and reports. Expert systems try to copy how human experts think to solve problems.
How Information Systems are Built
In big companies, information technology departments play a big role in how technology is developed and used. There are many ways to build and use an information system. Many developers use a step-by-step approach called the system development life cycle (SDLC). This process helps them build a system in stages:
- Planning
- Analyzing the system and its needs
- Designing the system
- Developing (building) it
- Putting parts together and testing
- Implementing (starting to use) and operating
- Maintaining (keeping it working)
Sometimes, a system is built within the company itself, or it can be outsourced, meaning another company builds it.
A computer-based information system is essentially a technology that records, stores, and shares information. It also helps draw conclusions from that information. Examples of new information systems include Geographic information systems (GIS), which deal with maps and location data. Building a system usually involves these steps:
- Understanding the problem and what's needed.
- Gathering information.
- Listing what the new system must do.
- Designing the system.
- Building the system.
- Putting the system into use.
- Reviewing and maintaining it.
Studying Information Systems
The field of "information systems" covers many topics. These include how to analyze and design systems, computer networks, keeping information secure, managing databases, and systems that help with decisions. "Information management" deals with how to collect and analyze information in a business. This includes using business tools, programming, e-commerce, and data mining. "Communications and networking" focuses on technologies that allow computers to talk to each other.
Information systems connects business and computer science. It uses ideas from information and computing to study business models and how to build IT systems. "Computer information systems" (CIS) looks at computers and how they process information, including their design and how they affect society. IS focuses more on what the system does, while CIS focuses more on how it's built.
Many experts agree that information systems is a mix of different fields like computer science, engineering, math, and management. An information system can also be defined as a collection of hardware, software, data, people, and procedures that work together to create good information.
Related Ideas
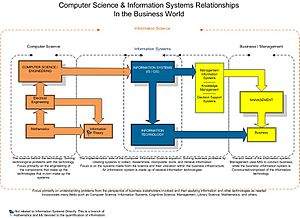
Just like computer science, other fields are related to information systems. The study of IS looks at how social and technical things affect how information systems are developed, used, and how they impact organizations and society. While these fields might overlap, they have different main goals.
Broadly, "information systems" is a scientific field that deals with how information is gathered, processed, stored, shared, and used in society and organizations. The term "information systems" also describes a job role in companies, governments, and non-profits.
"Information systems" often refers to how computer programs and technology interact. This can happen within a company or between different companies. An information system is the technology a company uses, and also how people interact with that technology to support the company's work. Information systems are different from information technology (IT) because an information system includes the IT part, but also how it works with business processes.
Some argue that focusing only on organizations limits the IS field. They suggest that IS should also look at how people use technology in social networking, gaming, or for personal use. Another way to tell IS apart from other fields is to ask: "What aspects of reality are most important in the IS field compared to others?" This helps define its purpose and role.
Business informatics is a similar field, especially popular in Europe. While "Information systems" often tries to explain things, "business informatics" focuses more on finding solutions and includes building and implementing technology.
Career Paths in Information Systems
People who study information systems can go into many different jobs:
- Information system strategy: Planning how a company uses its information systems.
- Management information systems (MIS): Helping with decision-making and managing information in a company.
- Project management: Leading teams to complete specific projects on time and within budget.
- Enterprise architecture: Designing how a whole company's technology and processes fit together.
- IS development: Building new information systems.
- IS consulting: Advising companies on their information systems.
- IS security: Protecting information systems from threats.
- IS auditing: Checking if information systems are working correctly and securely.
There are many job opportunities in information systems. People with special technical skills and good communication abilities will have the best chances. Those with management skills and an understanding of business will also do very well. Companies are increasingly using technology to help them make money.
Information technology is vital for modern businesses, so it offers many jobs. The information systems field includes the people who design and build systems, those who use them, and those who manage them. There's a high demand for IT staff like programmers, business analysts, and system designers. Many well-paying jobs exist in IT.
At the top of the list is the chief information officer (CIO). The CIO is the executive in charge of the IS department. In most companies, the CIO works closely with the CEO and CFO. This means they are actively involved in planning the company's future.
Research in Information Systems
Research in information systems often looks at how these systems affect people, groups, and organizations. Researchers categorize IS studies into two main types:
- Behavioral science: This aims to create and test ideas that explain or predict how people or organizations act.
- Design science: This focuses on creating new and smart tools or systems to improve what humans and organizations can do.
Researchers also look at different parts of information technology. They identify research outputs like:
- Constructs: These are the basic ideas or words used to describe problems and solutions in a field.
- Models: These are statements that show how different ideas are connected.
- Methods: These are the steps or guidelines used to do a task.
- Instantiation: This is when a new tool or system is actually built and used in its real environment.
Research activities include:
- Building a tool or system to do a specific task.
- Evaluating the tool to see if it works well.
- Theorizing and justifying why and how the tool worked (or didn't work) in its environment.
Even though information systems has been a field of study for over 30 years, researchers still debate its main focus. Some think it should focus only on the technology itself, while others believe it should look at how technology interacts with people and their surroundings. A third view suggests a balance between studying the technology and its context.
Since information systems is an applied field, people in the industry expect research to be immediately useful. However, IS researchers sometimes study human behavior in more detail than practitioners expect. This can make research results hard to understand and has led to some criticism.
In recent years, the role of the Information Systems Function (ISF) in businesses has grown a lot. It's now seen as key to increasing productivity and creating value. To study an information system itself, rather than just its effects, researchers use information systems models like EATPUT.
See also
 In Spanish: Sistema de información para niños
In Spanish: Sistema de información para niños
|
|
|
 | Sharif Bey |
 | Hale Woodruff |
 | Richmond Barthé |
 | Purvis Young |