Intermolecular force facts for kids
Intermolecular forces are special forces that act between molecules. Think of them as tiny invisible magnets that pull molecules closer or push them apart. These forces are much weaker than the strong chemical bonds that hold atoms together inside a molecule.
Even though they are weak, intermolecular forces are super important! They help explain why water is a liquid, why some things melt easily, and how many things work in your body.
What are Intermolecular Forces?
Imagine molecules as tiny building blocks. Intermolecular forces are the "glue" that holds these blocks together, but not as strongly as the "glue" inside each block (which are chemical bonds). These forces are responsible for many everyday things you see:
- Why water boils at 100°C and freezes at 0°C.
- Why oil and water don't mix.
- How geckos can stick to walls!
These forces can be short-range, meaning they only work when molecules are very close, or long-range, working over slightly larger distances.
Hydrogen Bonds
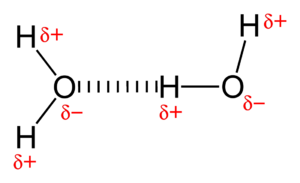
One of the most important types of intermolecular forces is called a hydrogen bond. This special force happens when a hydrogen atom, which is already connected to a very electronegative atom (like oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine), is also attracted to another electronegative atom in a different molecule.
Hydrogen bonds are stronger than other types of intermolecular forces. They are super important for life! For example, hydrogen bonds are why water has many of its unique properties, like being able to dissolve many substances and having a relatively high boiling point. They also play a huge role in the structure of DNA and proteins in your body.
Related pages
See also
 In Spanish: Fuerza intermolecular para niños
In Spanish: Fuerza intermolecular para niños
 | Lonnie Johnson |
 | Granville Woods |
 | Lewis Howard Latimer |
 | James West |