Kalmykia facts for kids
The Republic of Kalmykia (which is Республика Калмыкия in Russian and Хальмг Таңһч in Kalmyk) is a special part of Russia. It's like a state or province within the country. It is located in the Southern Federal District of Russia. Kalmykia was officially formed on November 4, 1920.
Its capital city is Elista.
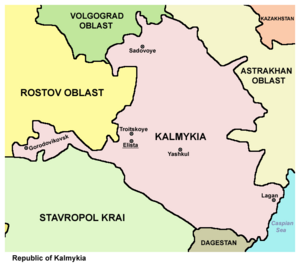
Kalmykia shares its borders with several other regions. To the south, it borders Stavropol Territory. The Republic of Dagestan is to the southeast. The Volgograd region is to the north, and the Astrakhan region is to the northeast. To the west, it borders the Rostov region.
Contents
Where is Kalmykia Located?
Kalmykia is in the very southeast of the European part of Russia. It stretches about 448 kilometers (278 miles) from north to south. From west to east, it is about 423 kilometers (263 miles) wide.
The region covers a large area of about 75,900 square kilometers (29,300 sq mi). This is bigger than countries like Belgium, Denmark, Switzerland, and the Netherlands combined!
Kalmykia's Natural Zones
Kalmykia has three main natural areas: western, central, and eastern.
- The western part includes the Gorodovikovsky and Yashaltinsky areas.
- The central part covers Maloderbetovsky, Sarpinsky, Ketchenerovsky, Virgin, Priyutnensky, and Iki-Burulsky areas.
- The eastern part includes October, Justinsky, Yashkulsky, Chernozemelsky, Lagansky, Dolbansky, and Limansky areas.
The western zone has the best soil and environmental conditions for farming.
A large part of the eastern zone is known as the "Black Earths." These areas have very fertile soil.
Kalmykia's Borders and Landscape
To the south, Kalmykia is bordered by the Kumo-Manych depression and the Manych and Kuma rivers. In the southeast, it touches the Caspian Sea. A small part of its northeastern border is near the Volga River. In the northwest, you can find the Ergeninsky height.
Most of Kalmykia is made up of flat plains. The northern part of the Near-Caspian lowland within Kalmykia is called the Sarpinsky lowland. The southern part has the Black Earths.
What Minerals Are Found in Kalmykia?
Kalmykia has supplies of oil and natural gas. The main known and used fields are Iki-Burulsky and Ermolinsky. These areas are part of the larger Near-Caspian gas and oil regions.
Kalmykia's Climate
Kalmykia has a very strong continental climate. This means its weather changes a lot between seasons. Summers are hot and very dry. Winters have little snow and can be very cold. The climate gets even more extreme as you move from west to east.
Winter Weather
In January, the average temperatures are below freezing. They range from about -7°C to -9°C (19-16°F) in the south and southwest. In the north, it gets colder, from -10°C to -12°C (14-10°F). The coldest temperatures can drop to -35°C to -37°C (-31 to -35°F) or even lower in northern areas. Sometimes, there are thaws in winter, and blizzards can happen. Ice can form, which is bad for farms, as it covers pastures and winter crops.
Summer Weather
Summers are long and warm, lasting about 240 to 275 days. In July, the average temperatures are around +23.5°C to +25.5°C (74-78°F). The hottest temperatures can reach +40°C to +44°C (104-111°F). Temperatures generally get warmer as you go from north to south and southeast in Kalmykia.
Dry Conditions
A special feature of Kalmykia's climate is its droughts and dry winds. There can be up to 120 dry, windy days in the summer. This makes Kalmykia one of the driest regions in the south of European Russia. The region gets only 210 to 340 millimeters (8-13 inches) of rain each year. Because of how much moisture it gets, Kalmykia has four main climate zones: very dry, dry, very droughty, and droughty.
Wind Energy
Kalmykia also has a lot of strong winds. This means it has great potential for wind energy. However, only a small amount of this energy is currently used by the Kalmyk Wind Power Station.
Nature and Wildlife in Kalmykia
Kalmykia is home to many different animals. About 60 types of mammals live here. Its lakes and rivers are important for birds. Around 130 kinds of birds nest in Kalmykia, and more than 50 kinds stop here during their yearly migrations. You can also find 20 types of reptiles and 3 types of amphibians.
Animals in Danger
Twenty-three types of birds found in Kalmykia are listed in the Red Book of the Russian Federation. This means they are rare or endangered and need protection.
Saiga Antelope
The number of saiga in Kalmykia changes, but it can be anywhere from 270,000 to 400,000 animals. These unique antelopes are a very important part of the region's wildlife.
Plants and Trees
Most of Kalmykia is a semi-desert zone. This means its plant life is a mix of steppe (grassland) and desert areas. Kalmykia is known as the most forestless region in Russia, meaning it has very few trees.
Images for kids
-
The Golden Temple in Elista.
See also
 In Spanish: Kalmukia para niños
In Spanish: Kalmukia para niños
 | Chris Smalls |
 | Fred Hampton |
 | Ralph Abernathy |