List of historical cuisines facts for kids
Have you ever wondered what people ate long, long ago? This article explores the fascinating world of historical cuisines. These are the unique ways people cooked and ate in different parts of the world throughout history. From ancient empires to more recent times, food tells us a lot about how people lived, what was important to them, and what ingredients were available.
Contents
Food Across Ancient Continents
Food has always been a central part of human life. It's not just about eating; it's about culture, survival, and even celebration. Let's explore some of the interesting food traditions from different continents.
African Food History
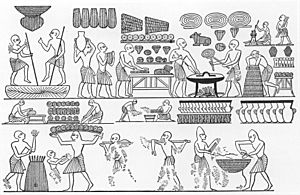
Africa is a huge continent with a very long history. One of the most famous ancient food cultures comes from Ancient Egyptian cuisine.
- Ancient Egyptian Cuisine: The people of ancient Egypt ate a lot of bread and beer, which they made from grains like barley and wheat. They also enjoyed vegetables, fruits, fish from the Nile River, and some meat. Food was so important that scenes of cooking and eating are found in their tombs!
Early American Cuisines
Before European settlers arrived, many different groups of Native American people lived across the Americas. Each group had its own unique way of finding and preparing food.

- Native American Cuisine: This includes many different styles of cooking from various tribes. They used local plants and animals. For example, corn, beans, and squash were very important crops.
- Aztec Cuisine: The Aztecs, who lived in what is now Mexico, relied heavily on corn. They made tortillas and tamales. They also ate beans, squash, chili peppers, and even insects!
- Maya Cuisine: Like the Aztecs, the Maya people of Central America also used corn as a main food. They also grew cacao (for chocolate), avocados, and various fruits.
- Inca Cuisine: In the Andes Mountains of South America, the Inca empire had a diet based on potatoes and quinoa. They also raised llamas and alpacas for meat and transport.
- Muisca Cuisine: The Muisca people, from what is now Colombia, also grew corn, potatoes, and quinoa. They were skilled farmers who used terraces to grow crops on mountainsides.
- Cuisine of the Thirteen Colonies: When European settlers came to North America, they brought their own cooking traditions. But they also learned to use new ingredients from the Native Americans, like corn, pumpkins, and turkeys.
- Cuisine of Antebellum America: This refers to the food eaten in the United States before the Civil War (1861-1865). It was a mix of European traditions and local ingredients, often influenced by the foods grown on plantations.
- History of Argentine Cuisine: In South America, Argentina's food history is a blend of native traditions and influences from Spanish and Italian immigrants. Meat, especially beef, became a very important part of their diet.
Asian Food Traditions
Asia is the largest continent, with a rich and diverse history of food. Many ancient civilizations developed unique cooking styles here.
- Iranian Cuisine: The food of Iran has a long history, with influences from ancient Persia. Rice, bread, fresh herbs, and various meats are common.
- Ancient Israelite Cuisine: The people of ancient Israel ate foods mentioned in the Bible, like bread, olives, figs, grapes, and lentils. They also raised sheep and goats.
- Byzantine Cuisine: The Byzantine Empire, which lasted for over a thousand years, had a cuisine that blended Roman and Greek traditions with influences from the Middle East. Fish, vegetables, and olive oil were important.
- Hittite Cuisine: The Hittites were an ancient people in Anatolia (modern-day Turkey). Their diet included grains, legumes, and fruits. They also had a special type of bread.
- History of Chinese Cuisine: China has one of the oldest and most varied food histories in the world. Different regions developed unique dishes using ingredients like rice, noodles, pork, and various vegetables.
- History of Indian Cuisine: India's food history is incredibly rich, with a wide range of spices, grains, and cooking methods. Different regions have very distinct culinary traditions.
- Ottoman Cuisine: The Ottoman Empire, which ruled a vast area for centuries, had a cuisine that mixed influences from Central Asia, the Middle East, and the Mediterranean. Kebabs, pastries, and rich stews are famous.
European Food Through Time
Europe has seen many changes in its food over thousands of years, from ancient empires to modern nations.

- Ancient Greek Cuisine: The ancient Greeks ate a simple diet of bread, olives, figs, and cheese. They also enjoyed fish and some meat. Wine was a common drink.
- Ancient Roman Cuisine: The Romans had a more complex diet than the Greeks. While common people ate simple meals, the wealthy enjoyed elaborate feasts with many courses, including exotic ingredients.
- Medieval Cuisine: During the Middle Ages, food in Europe varied greatly between the rich and the poor. Grains like wheat and barley were staples. Spices were very expensive and used by the wealthy.
- Early Modern European Cuisine: From the 1500s to the 1700s, new foods like potatoes and tomatoes arrived from the Americas, changing European diets forever. Sugar also became more common.
- Soviet Cuisine: In the 20th century, the Soviet Union developed a cuisine influenced by its many different republics. Simple, hearty dishes like borscht (beet soup) and pelmeni (dumplings) were common.
See also
- Food history
- List of ancient dishes
- Paleolithic diet
- Timeline of food


