Low-pass filter facts for kids
A low-pass filter is an electronic tool that lets some signals pass through easily while blocking others. Think of it like a special gate for sounds or electrical signals. It allows signals with a low frequency to pass, but it stops or greatly reduces signals with a high frequency.
Imagine you're listening to music. A low-pass filter would let the deep bass sounds (low frequencies) come through clearly, but it would make the high-pitched sounds (high frequencies) much quieter or even silent.
Contents
What is a Low-Pass Filter?
A low-pass filter is a type of electronic circuit that works with different frequencies. Frequencies are like how fast something vibrates. For sound, low frequencies are deep sounds, and high frequencies are squeaky sounds. For electricity, it's how fast the electrical signal changes direction.
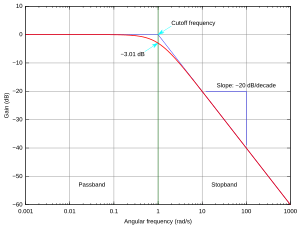
This filter has a special point called the cutoff frequency. Any signal that has a frequency below this cutoff point can pass through the filter easily. But if a signal's frequency is above this cutoff, the filter will block it, making it much weaker or almost disappear.
How Do Low-Pass Filters Work?
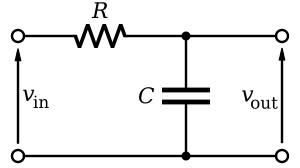
Low-pass filters are built using basic electronic parts like resistors and capacitors. These parts work together to decide which frequencies get through and which don't.
- Resistors resist the flow of electricity.
- Capacitors store electrical energy and can block direct current (DC) while allowing alternating current (AC) to pass, especially higher frequencies.
In a simple low-pass filter, the capacitor helps to "short-circuit" or divert the high-frequency signals away from the output, while the low-frequency signals can still pass through to where they are needed.
Passive vs. Active Filters
There are two main types of low-pass filters:
- Passive filters use only basic parts like resistors, capacitors, and inductors. They don't need extra power to work.
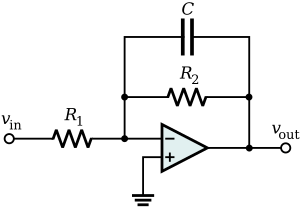
- Active filters use extra electronic parts like operational amplifiers (Op-Amps). These filters need power to work, but they can be more powerful and precise.
Where Are Low-Pass Filters Used?
Low-pass filters are used in many everyday technologies. They help make sure that only the right signals get through, improving sound quality or making electronic devices work correctly.
In Audio Systems
- Speakers: In speaker systems, low-pass filters send the low-frequency sounds (bass) to the large woofer speakers. This makes the bass sound clear and deep, without high-pitched sounds coming from the wrong speaker.
- Subwoofers: A subwoofer is a speaker designed only for very low bass sounds. It uses a low-pass filter to make sure it only plays those deep notes.
- Music Production: Music producers use low-pass filters to shape sounds, remove unwanted noise, or create special effects.
In Electronics and Communication
- Radio and TV: Low-pass filters help to remove unwanted noise or interference from radio and television signals, making the picture and sound clearer.
- Data Transmission: When sending data over cables, low-pass filters can help smooth out the signal and remove high-frequency noise that could corrupt the data.
- Medical Devices: In medical equipment, these filters can help clean up signals from the body, like electrocardiograms (ECGs), so doctors can see clear heart activity without interference.
Related pages
See also
 In Spanish: Filtro paso bajo para niños
In Spanish: Filtro paso bajo para niños