Markov chain facts for kids
A Markov chain is a special kind of model. It helps us understand things that happen randomly over time. Imagine a game where what happens next only depends on where you are right now. It doesn't matter how you got there. That's the main idea behind a Markov chain!
These models are named after a rule called the Markov property. This rule says that the future of a process depends only on its current "state." It doesn't remember anything that happened before. Think of it like a game of "hot potato." The next person to get the potato only depends on who has it right now, not who had it five turns ago.
Markov chains can move forward in different ways:
- Discrete Time: This means the process moves in clear, separate steps. Think of it like a clock ticking second by second (t = 1, t = 2, t = 3, and so on). The chance of moving from one state to another only depends on the state it's in at that exact step.
- Continuous Time: Here, the process can change at any moment, not just at fixed steps. Imagine a stopwatch running smoothly. The time spent in each state is random. It's often based on something called an exponential distribution. This means there's an average time a system might stay in a state, but it can vary.
Contents
How Markov Chains Work
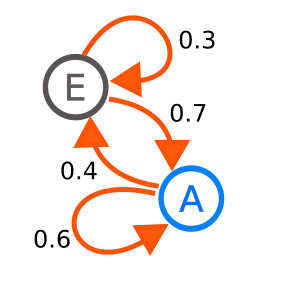
Markov chains help us predict what might happen next in a random process. They do this by looking at the chances (or probabilities) of moving from one "state" to another. A "state" is just a way of describing how the system is right now.
For example, imagine a simple weather model. The weather can be either "sunny" or "cloudy."
- If it's sunny today, there's a 90% chance it will be sunny tomorrow.
- If it's cloudy today, there's a 60% chance it will be cloudy tomorrow.
This is a Markov chain because tomorrow's weather only depends on today's weather. It doesn't matter if it was sunny all week before that.
A Creature's Eating Habits: An Example
Let's look at a fun example to understand Markov chains better. Imagine a creature that eats only three things: grapes, cheese, or lettuce. This creature eats exactly once a day. Its eating choices follow these rules:
- If it ate cheese yesterday: It will eat lettuce or grapes today. The chance for each is equal (50% for lettuce, 50% for grapes). It will never eat cheese again today.
- If it ate grapes yesterday: It has a small chance (10%) of eating grapes again today. It has a 40% chance of eating cheese. And it has a 50% chance of eating lettuce.
- If it ate lettuce yesterday: It won't eat lettuce again today. It will eat grapes with a 40% chance or cheese with a 60% chance.
This creature's eating habits can be modeled with a Markov chain. Why? Because its choice for today only depends on what it ate yesterday. It doesn't care what it ate two, three, or more days ago. Using a Markov chain, we could even figure out how often this creature would eat cheese over a very long time!
Who Invented Markov Chains?
Markov chains are named after a brilliant Russian mathematician named Andrey Markov. He was born in 1856 and passed away in 1922. Markov did a lot of important work in the field of probability theory. His ideas about these chains have become very useful in many different areas of science and technology.
Where Are Markov Chains Used?
Markov chains are not just for fun examples about eating habits! They are used in many real-world situations:
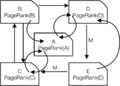
- Google's PageRank: One of the most famous uses is in Google's original PageRank algorithm. This algorithm helps Google decide which web pages are most important. It treats web pages as "states" and links between them as "transitions" in a Markov chain.
- Weather Forecasting: Scientists use them to model weather patterns and predict future weather.
- Genetics: They help understand how genes change over time.
- Speech Recognition: Your phone or computer might use Markov chains to understand what you're saying.
- Finance: They can model how stock prices might change.
- Games: Even some board games or video games can be analyzed using Markov chains to understand possible outcomes.
These models are powerful tools for understanding systems where the future depends on the present, but not on the entire past history.
Images for kids
-
Russian mathematician Andrey Markov
See also
 In Spanish: Cadena de Márkov para niños
In Spanish: Cadena de Márkov para niños
 | Frances Mary Albrier |
 | Whitney Young |
 | Muhammad Ali |