Exponential distribution facts for kids
The exponential distribution is a special way to understand how long we might have to wait for something to happen. Imagine you're waiting for a bus, or for a light bulb to burn out. The exponential distribution helps us guess how long these random waits might be. It's used a lot in real life, especially when we want to know how long things last or how much time passes between events.
This type of distribution is all about positive numbers, meaning it deals with time or distances that are always more than zero. It's like a continuous version of another idea called the geometric distribution, which looks at how many tries it takes for something to happen.
Here are some cool examples where the exponential distribution can be helpful:
- How long a phone call might last.
- The time it takes to fix something at a service center.
- The time between two phone calls coming into a call center.
- How long it takes for half of a group of atoms to decay (this is called half-life).
- How long electronic parts are expected to work before they break down. This is often called Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF).
- How old plants or animals might get.
- Simple ways insurance companies guess how long people might live or how often accidents happen.
What is a Probability Distribution?
A probability distribution is like a map that shows all the possible outcomes of a random event and how likely each outcome is. For example, if you flip a coin, the outcomes are "heads" or "tails," and a probability distribution would show that each has a 50% chance.
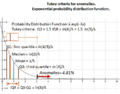
The exponential distribution is a "continuous" probability distribution. This means it can describe events that can take any value within a range, like time. Time doesn't just jump from 1 second to 2 seconds; it can be 1.5 seconds, 1.501 seconds, and so on.
How It's Used
The main use of the exponential distribution is to figure out the length of random time periods. It's very useful in areas like:
- Reliability engineering: This is about how long products or systems work without failing. Companies use it to predict how long a computer part or a car engine might last.
- Queuing theory: This studies waiting lines. For example, how long you might wait in line at a store or for a roller coaster.
- Physics: It helps understand how long it takes for radioactive materials to decay.
Related Ideas
- Normal distribution: This is another very common probability distribution, often called the "bell curve." It describes things like people's heights or test scores, where most values are around the average, and fewer values are at the extremes.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Distribución exponencial para niños
In Spanish: Distribución exponencial para niños