Meristem facts for kids
A meristem is a special part of a plant that has cells that are always dividing. Think of them as the plant's growth factories! These cells are found in areas where the plant needs to grow, like the tips of its roots and shoots.
Most plant cells, once they are fully grown and have a specific job (like being part of a leaf or a stem), can't divide anymore. But meristem cells are different. They are like stem cells in animals because they haven't decided what they want to be yet, and they can keep dividing to make new cells. This constant division helps the plant grow new tissues and parts, like new leaves, stems, and roots.
Meristem cells are usually small and full of protoplasm (the living stuff inside a cell). They have tiny vacuoles (storage sacs) and don't have fully developed chloroplasts yet, but they have the basic parts that will become chloroplasts later. These cells are packed tightly together, with no gaps between them, and their cell walls are very thin.
Contents
What is an Apical Meristem?
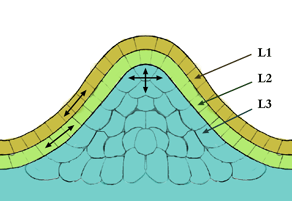
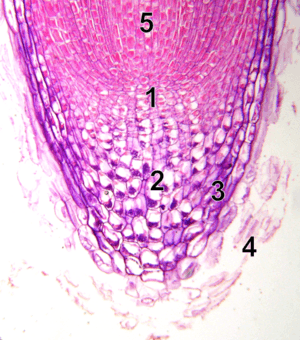
The apical meristem is like the main growth engine of a plant. You can find it at the very tips of a plant's roots and shoots (stems).
This meristem is responsible for the plant's first type of growth, called primary growth. It helps young seedlings start growing and keeps pushing new growth forward. For example, as a root grows deeper into the soil, the apical meristem at its tip is constantly making new cells behind it, pushing the tip forward. Apical meristems are quite small compared to other growth areas.
Primary Meristems: Making Plants Taller
Apical meristems can develop into three main types of primary meristems. These are all about making the plant grow longer or taller:
- Protoderm: This layer is on the outside of the stem and root. It develops into the epidermis, which is the plant's outer skin, protecting it.
- Procambium: Found just inside the protoderm, this meristem develops into the plant's main transport systems: primary xylem and primary phloem. Xylem carries water, and phloem carries food. It also helps create another type of meristem later, called the vascular cambium.
- Ground meristem: This meristem develops into the inner parts of the stem and root, like the pith (the central part of a stem). It also helps create the cork cambium, which is another important growth area.
These primary meristems are responsible for the plant's primary growth, which means increasing its length or height.
Secondary Meristems: Making Plants Wider
These meristems are responsible for secondary growth, which means making the plant grow wider or thicker. There are two main types:
- Vascular cambium: This meristem creates more xylem and phloem, but this time it's called secondary xylem and secondary phloem. In many plants, especially trees, this is what forms the wood. Plants that produce wood are called arborescent plants. You won't find this type of growth in small, soft plants like herbaceous plants.
- Cork cambium: This meristem is responsible for creating the outer protective layer of a tree, which we know as the bark.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Complex leaves of Cardamine hirsuta result from KNOX gene expression
See also
 In Spanish: Meristemo para niños
In Spanish: Meristemo para niños
 | Lonnie Johnson |
 | Granville Woods |
 | Lewis Howard Latimer |
 | James West |