Newton (unit) facts for kids
The newton (symbol: N) is the main unit of force in the SI system. It's named after Sir Isaac Newton because of his important work on how things move.
A newton tells us how much force is needed to make a mass of one kilogram speed up (or accelerate) at a rate of one metre per second every second. Imagine pushing something: the harder you push, the more newtons of force you are applying!
Here's the science way to write it: 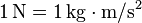
Contents
What Does One Newton Feel Like?
To help you understand how much force one newton is:
- One newton is about the force of Earth's gravity pulling on a small apple that weighs around 102 grams.
- If you hold a 1-kilogram object (like a liter bottle of water) on Earth, it pushes down with a force of about 9.8 newtons.
- In the US Customary Unit system, force is measured in pounds (symbol: lbf). One pound is equal to about 4.448 newtons.
How the Newton Became a Standard Unit
In 1946, a group called the Conférence Générale des Poids et Mesures (CGPM) decided that the unit of force should be the amount needed to make 1 kilogram of mass accelerate at 1 meter per second, every second. Then, in 1948, this group officially named this unit the "newton." This decision helped make the newton the standard unit of force in what we now call the SI system.
Why is "Newton" Sometimes Capitalized?
The SI unit is named after Isaac Newton. When we write the symbol for the newton, we use a capital "N" (like in 10 N). This is because it's named after a person. However, when you write out the full word "newton," it usually starts with a lowercase letter (like "five newtons"). The only time "newton" would start with a capital letter is if it's at the beginning of a sentence or in a title.
Newton's Second Law of Motion
Sir Isaac Newton's second law of motion explains the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. It's often written as: F = ma
- F stands for the force applied (measured in newtons).
- m stands for the mass of the object (measured in kilograms).
- a stands for the acceleration of the object (measured in meters per second squared).
This law means that if you apply more force to an object, it will accelerate more. Also, if an object has more mass, you'll need more force to make it accelerate at the same rate.
Images for kids
-
A carabiner used in rock climbing. It has different safety ratings in newtons depending on how it's loaded. For example, it can hold 26,000 newtons (26 kN) when loaded along its spine with the gate closed.
See also
 In Spanish: Newton (unidad) para niños
In Spanish: Newton (unidad) para niños


