North Carolina General Assembly facts for kids
Quick facts for kids North Carolina General Assembly |
|
|---|---|

Seal of the North Carolina General Assembly
|
|
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Houses | Senate House of Representatives |
| History | |
| Founded | May 20, 1775 |
| Leadership | |
|
President of the Senate &
Lieutenant Governor |
Mark Robinson (R)
Since January 9, 2021 |
|
President pro tempore of the Senate
|
Phil Berger (R)
Since January 26, 2011 |
|
Speaker of the North Carolina House of Representatives
|
Tim Moore (R)
Since January 15, 2015 |
| Structure | |
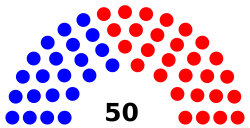
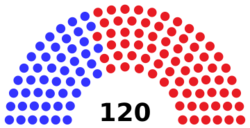
| Seats | 170 voting members
|
 |
|
|
Senate political groups
|
|
 |
|
|
House of Representatives political groups
|
|
| Elections | |
|
Last general election
|
November 8, 2022 |
|
Next general election
|
November 5, 2024 |
| Meeting place | |
 |
|
| North Carolina Legislative Building Raleigh |
|
The North Carolina General Assembly is the main law-making body for the state of North Carolina. It is a bicameral legislature, meaning it has two parts. These two parts are the Senate and the House of Representatives. The General Assembly meets in the North Carolina State Legislative Building in Raleigh, the state capital.
This assembly creates and passes the state laws of North Carolina. These laws are also known as the General Statutes. Since 1868, the House of Representatives has had 120 members. The Senate has 50 members. There are no limits on how many terms a person can serve in either part of the assembly. Both parts of the assembly serve two-year terms. Currently, the Republican Party controls both the Senate and the House. They have enough votes to overrule a governor's veto.
Contents
History of North Carolina's Lawmakers
Early Days: Colonial Period
In 1663, King Charles II of England gave a special paper, called a royal charter, to eight men. These men were called lords proprietor. They were to start a colony in North America called Carolina. The plan was for a governor, a council, and an assembly to run the colony. The assembly would make laws.
The first assembly meeting happened in 1665. It was for Albemarle County. This group was called the General Court and Committee. They made laws, set taxes, and created courts. They also decided where towns and ports would be. Laws they passed lasted 18 months. Then, they were sent to England for approval.

After 1731, the British king had more control. Governors received secret instructions from England. These instructions often caused problems with the General Assembly. The assembly controlled the colony's money. They used this power to get governors to agree with them. They would sometimes hold back salaries or funds. This showed the assembly was fighting for the colonists' interests. This tension helped lead to North Carolina breaking away from Great Britain.
Becoming a State: Revolution and Early Years
In 1774, colonists elected a provincial congress. This was a group separate from the royal governor. It was the start of the American Revolution. The fifth Congress approved North Carolina's first constitution in 1776.
After the United States Declaration of Independence, each former colony became an independent state. North Carolina's new constitution made the General Assembly very powerful. Its members were elected by the people. This assembly would then choose the state's governor and judges. The governor had less power. They needed the assembly's approval for many important actions.
The first General Assembly met on April 7, 1777. It met in New Bern, North Carolina. The Senate had one member from each county. The House of Commons had two members from each county. Only men who owned land and were Protestant could serve.
For many years, the General Assembly met in different towns. These included New Bern, Hillsboro, and Fayetteville. In 1794, it finally met in the new state capital, Raleigh. It has met there ever since.

In 1835, the state constitution was updated. The governor would now be elected by the people. But the assembly still elected other officials. The number of senators was set at 50. The number of representatives (then called commoners) was set at 120. Senators were elected from districts with similar populations. House members were still elected by county. Counties with more people got more representatives.
Modern Era: 20th Century Changes
In 1921, Lillian Exum Clement became the first woman to join the General Assembly.
Over time, North Carolina's population changed. More people moved to cities. But the way representatives were chosen still favored rural areas. This meant cities were not fairly represented. In 1966, the U.S. Supreme Court made a ruling. It said that state legislative districts must have roughly equal populations. This is known as "one man, one vote". This change meant that urban areas finally got fair representation. It also meant some smaller counties were combined into larger districts.
A new building for the legislature was finished in 1963. The General Assembly held its first meeting there on February 6. This new building is the North Carolina State Legislative Building.
In the 1970s, lawmakers worked to make the General Assembly stronger. They hired their own research staff. They also tried to appoint their own members to state boards. However, the North Carolina Supreme Court said this was not allowed in 1982. In 1977, the state constitution was changed. This allowed governors and lieutenant governors to serve a second term.
Who Are the Members?
The General Assembly has 170 elected members. There are 120 members in the House of Representatives. There are 50 members in the Senate. Each member represents a specific area, called a district. Members are elected every two years in even-numbered years. Their terms start in January after their election.
North Carolina's assembly is like a "citizen legislature". This means being a lawmaker is considered a part-time job. Members receive a yearly salary. They also get money for daily expenses and travel. If they vote to increase their pay, it does not take effect until after the next election. If a seat becomes empty, the governor appoints someone. This person is chosen by the political party of the person who left the seat.
How the Assembly Works
Each part of the legislature has leaders.
- The Senate is led by the President of the Senate. This job is held by the lieutenant governor. The President guides debates and keeps order. They can only vote if there is a tie. The Senate also elects a President pro tempore. This person appoints the Senate's committees.
- The House of Representatives is led by the Speaker. The Speaker appoints the House's committees. The House also elects a Speaker pro tempore. Both the Speaker and Speaker pro tempore are chosen by the House members.
Both the Senate and House have other important staff. They have a principal clerk who keeps records. A reading clerk reads documents. A sergeant at arms helps keep order.
Special groups called standing committees look at new laws. They hold meetings and suggest changes. All new laws must be checked by a rules committee. Then, they are voted on by the full Senate or House.
What Powers Does the Assembly Have?
The North Carolina constitution gives the General Assembly the power to make state laws. These laws can be for the whole state or just for specific counties or towns. All laws must start with "The General Assembly of North Carolina enacts:".
The assembly can also set taxes and approve the state budget. There are special rules for passing money bills. They must be read three times on different days. The votes of each lawmaker must be recorded. Money bills must also say what the money is for.
The governor signs bills they approve into law. They can also veto bills they do not approve. But the General Assembly can overrule a veto. They need a three-fifths majority vote to do this. The governor cannot veto local bills or decisions about how districts are drawn. The two houses can also pass joint resolutions. These are not subject to a governor's veto.
The assembly also watches over state government agencies. They can change the governor's orders about how agencies are organized. They can also get documents from agencies and inspect their buildings. All legislative committees can ask people to testify and provide documents.
The House of Representatives can also impeach (accuse) elected state officials. If an official is impeached, the Senate holds a trial. They can remove an official from office with a two-thirds vote.
The General Assembly is the only group that can suggest changes to the state constitution. If three-fifths of both the House and Senate agree, the change is put to a statewide vote. The governor cannot veto these constitutional changes.
When Does the Assembly Meet?
The General Assembly meets regularly. The "long session" starts in January of odd-numbered years. It usually lasts about six months. Then, they meet again the following even-numbered year for the "short session". This usually lasts about six weeks.
The governor can call special meetings if needed. A majority of members must be present for business to be done. When meeting, both the House and Senate usually meet on Monday evenings and during the day on Tuesdays, Wednesdays, and Thursdays. Committee meetings are usually in the mornings and late afternoons.
The meetings of each house are written down in official journals. These are published after each session. The public can watch the sessions from a special viewing area called a gallery.
Support for Lawmakers
The General Assembly has many staff members who help them. These staff work in the Legislative Building and the Legislative Office Building. Each lawmaker has at least one assistant or clerk. These assistants help with schedules, talk to people from their district, and give advice on laws. The North Carolina General Assembly Police protect the members and buildings.
See also
 In Spanish: Asamblea General de Carolina del Norte para niños
In Spanish: Asamblea General de Carolina del Norte para niños
Images for kids
 | Sharif Bey |
 | Hale Woodruff |
 | Richmond Barthé |
 | Purvis Young |





