Olmec heartland facts for kids

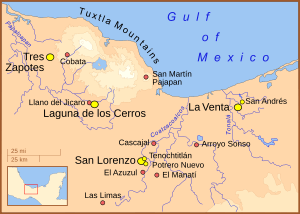
The Olmec heartland is a very important part of southern Mexico. It's located on the Gulf Coast, between the Tuxtla mountains and the ancient Olmec city of La Venta. This area reaches about 80 kilometers (50 miles) inland from the Gulf of Mexico.
Today, just like in ancient times, the Olmec heartland is a tropical forest with many winding rivers. Most experts believe this region was the birthplace of the Olmec culture. The Olmec civilization became very important across Mesoamerica from about 1400 BCE until 400 BCE. This area is also sometimes called Olman or the Olmec Metropolitan Zone.
Contents
Major Olmec Cities
The Olmec heartland was home to several large and important ancient cities. These cities were centers of Olmec life, art, and power.
San Lorenzo Tenochtitlán
San Lorenzo Tenochtitlán was one of the earliest and most powerful Olmec cities. It was a major center for hundreds of years. Many large stone sculptures, like the famous colossal heads, were found here.
La Venta
La Venta became a very important Olmec city after San Lorenzo. It had a large pyramid and many impressive stone monuments. La Venta was a key center for trade and religious ceremonies.
Tres Zapotes
Tres Zapotes was another significant Olmec site. It was active for a long time, even after the main Olmec period. Important Olmec artifacts and carvings have been discovered there.
Laguna de los Cerros
Laguna de los Cerros is also considered a major Olmec site. However, less research has been done here compared to the other big cities. It was likely an important regional center.
Smaller Olmec Sites
Besides the major cities, there were also smaller Olmec sites in the heartland. These places often had special purposes or were part of the larger Olmec network.
- El Manatí was a unique Olmec site. It was a sacred bog where people placed offerings, including wooden sculptures and rubber balls.
- El Azuzul is located close to the San Lorenzo area. It's known for finding twin statues that look like "The Wrestler."
- San Andrés is a site found near La Venta. It has provided clues about early Olmec writing.
Important Discoveries
Some amazing Olmec artifacts have been found in the heartland, even if they weren't directly linked to a known ancient city. These finds help us understand the Olmec people better.
- "The Wrestler" is a famous basalt statue. It was found at a place called Arroyo Sonso. This statue shows a person in a dynamic pose, almost like a wrestler.
- Las Limas Monument 1 is a significant stone sculpture. It was discovered by two children who were looking for nuts! This monument shows a young man holding a baby-like figure.
- San Martín Pajapan Monument 1 was found high up on the slopes of San Martin Pajapan mountain. It's a large stone sculpture of a ruler or important person.
See also
 In Spanish: Área nuclear olmeca para niños
In Spanish: Área nuclear olmeca para niños
 | William Lucy |
 | Charles Hayes |
 | Cleveland Robinson |