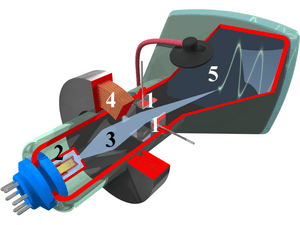
Illustration showing the interior of a cathode ray tube for use in an oscilloscope. Numbers in the picture indicate:
- Deflection voltage electrodes
- Electron gun
- Electron beam
- Focusing coil
- Phosphor-coated inner side of the screen

A Tektronix model 475A portable analogue oscilloscope, typical of the late
1970s. This dual-trace, dual-sweep instrument had a horizontal bandwidth of 250
MHz, a maximum vertical sensitivity of 5
mV per division, and maximum (unmagnified) horizontal sweep speed of 10
ns per division. The vertical controls are on the left with Channel 1 above and Channel 2 below. The horizontal sweep controls are on the right with the Main Trigger above and the Delayed Trigger below. The
CRT controls are below the screen. The metal loop to the lower right of the screen provided a calibration signal for voltage and current probes.
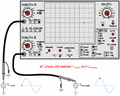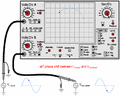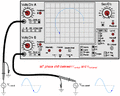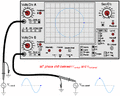
An oscilloscope (sometimes abbreviated CRO, for cathode ray oscilloscope, or commonly just scope or O-scope) is a piece of electronic equipment that lets you see changes in signal voltage. For example, if you want to see the signal a small electronic timer was producing, you could connect it to an oscilloscope and see.
Usually, it shows a two-dimensional graph of one or more electrical potential differences (vertical axis). These graphs are plotted with time or of some other voltage along horizontal axis.
Description
A typical oscilloscope is usually box shaped with a display screen, numerous input connectors, control knobs and buttons on the front panel. To aid measurement, a grid called the graticule is drawn on the face of the screen. Each square in the graticule is known as a division.
Images for kids
-
A Tektronix model 475A portable analog oscilloscope, a typical instrument of the late 1970s
-
Oscilloscope cathode-ray tube
-
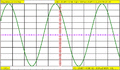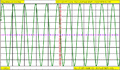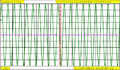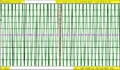
Computer model of the impact of increasing the timebase time/division
-
Type 465 Tektronix oscilloscope. This was a popular analog oscilloscope, portable, and is a representative example.
-
A 24-hour clock displayed on a CRT oscilloscope configured in X-Y mode as a vector monitor with dual R2R DACs to generate the analog voltages
-
A computer model of the sweep of the oscilloscope
-
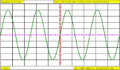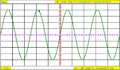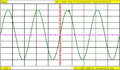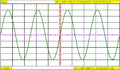
Lissajous figures on an oscilloscope, with 90 degrees phase difference between x and y inputs
-
Example of an analog oscilloscope Lissajous figure, showing a harmonic relationship of 1 horizontal oscillation cycle to 3 vertical oscillation cycles
-
For analog television, an analog oscilloscope can be used as a vectorscope to analyze complex signal properties, such as this display of SMPTE color bars.
-
Digital 4-channel oscilloscope monitoring a boost converter
-
PicoScope 6000 digital PC-based oscilloscope using a laptop computer for display & processing
-
-
-
Sum of a low-frequency and a high-frequency signal
-
-
Dual trace, showing different time bases on each trace
See also
 In Spanish: Osciloscopio para niños
In Spanish: Osciloscopio para niños

 In Spanish: Osciloscopio para niños
In Spanish: Osciloscopio para niños