Phonetics facts for kids
Phonetics is the science that studies the sounds of human speech. The word "phonetics" comes from the Greek word phone, which means 'sound' or 'voice'. Someone who is an expert in phonetics is called a phonetician.
Phonetics looks at how speech sounds (called phones) are made, how we hear them, and how we understand them. It's closely related to Phonology, which studies how sounds are organized into systems and units, like phonemes (the smallest sound units that change meaning). Phonetics is one of the main parts of orthographical linguistics, which is the study of how language is written. It's different from grammar (how words are put together) and lexis (the words themselves).
Contents
What are the Main Types of Phonetics?
Phonetics is usually divided into three main areas, each focusing on a different part of how speech sounds work:
How We Make Sounds: Articulatory Phonetics
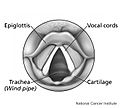
- articulatory phonetics studies how we use our mouths, tongues, lips, and vocal cords to make speech sounds. It looks at where sounds are made in our vocal tract and how our speech organs move.
How Sounds Travel: Acoustic Phonetics
- acoustic phonetics focuses on the physical properties of speech sounds as sound waves. It examines things like the pitch, loudness, and length of sounds, and how our inner ear picks them up.
How We Understand Sounds: Auditory Phonetics
- auditory phonetics explores how our brains process and understand the sounds our ears hear. It's all about how we perceive and interpret speech.
The International Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Association (IPA) has identified more than 100 different speech sounds. They have a special writing system called the International Phonetic Alphabet (also known as the IPA). This alphabet has a unique symbol for almost every sound found in human languages around the world. This makes it a very useful tool for linguists, language learners, and speech therapists.
The History of Phonetics
The study of phonetics began a very long time ago, about 2,500 years ago, in what is now India. A famous scholar named Pāṇini wrote an important essay about Sanskrit linguistics in the 5th century BC. In his work, he described exactly where and how consonant sounds were made in Sanskrit. Even today, the major writing systems in India arrange their consonants in a similar way to how Pāṇini organized them.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Fonética para niños
In Spanish: Fonética para niños
 | Percy Lavon Julian |
 | Katherine Johnson |
 | George Washington Carver |
 | Annie Easley |