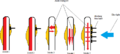Phototropism facts for kids

Phototropism is how plants and some other living things grow towards or away from light. Think of a sunflower turning to face the sun! This amazing ability helps plants get enough sunlight for food. It's all thanks to a special plant chemical called auxin.
Contents
What is Phototropism?
Phototropism is a type of tropism. A tropism is when a living thing grows or moves in response to something outside of it. For phototropism, that "something" is light.
- When a plant grows towards a light source, it's called positive phototropism. Most plant stems and leaves show positive phototropism. They need sunlight to make their food.
- When a plant grows away from light, it's called negative phototropism. Plant roots often show negative phototropism. They usually grow down into the soil, away from the light. Some climbing plants also grow away from light to find dark objects to climb on.
How Plants Bend Towards Light
Plants bend towards light because of a special plant hormone called auxin. Hormones are like chemical messengers in living things.
Auxin's Role in Growth
Auxin is made in the tips of plant stems. When light shines on a plant stem, the auxin moves to the side of the stem that is in the shade.
- On the shaded side, auxin makes the cells grow longer and faster.
- On the side facing the light, the cells grow more slowly.
Because the shaded side grows faster, it pushes the stem to bend towards the light. This helps the plant get more sunlight for photosynthesis, which is how plants make their food.
Light Receptors in Plants
Plants have special parts that can "see" light. These are called light receptors. They help the plant know where the light is coming from.
- Phototropins are receptors that mostly sense blue light. They are very important for phototropism in plants like Arabidopsis thaliana.
- Phytochromes are receptors that sense red light. They help plants know if it's day or night and when to flower.
- Cryptochromes also sense blue light. They help with many plant processes, including how plants grow and develop.
These receptors work together to help the plant respond correctly to different kinds of light.
Images for kids
-
Daisies (Bellis perennis) facing the sun after opening in the morning, and they follow the sun through the day
-
Ravenalas growing between two buildings in Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of Congo. The plane (here perpendicular to the north-south axis) of these two plants is orientated to maximize daylight absorption
See also
 In Spanish: Fototropismo para niños
In Spanish: Fototropismo para niños