Polar circle facts for kids
Imagine invisible lines on Earth that mark the coldest parts of our planet! These are called polar circles. They are important geographic lines that help us understand Earth's climate zones. There are two main polar circles: the Arctic Circle in the north and the Antarctic Circle in the south.
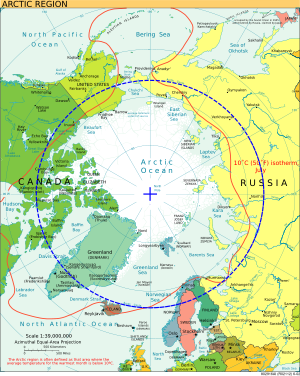
These circles are key circles of latitude, also known as parallels. They are slowly moving. The Arctic Circle is currently moving north by about 14.5 meters each year. It is now at a mean latitude of about 66.56 degrees North. The Antarctic Circle is moving south by the same amount. It is now at a mean latitude of about 66.56 degrees South.
Polar circles are often linked to the polar regions. These areas have a very cold climate. Most of the Arctic Circle is ocean, with few people living there. Antarctica, which is mainly land and ice, has no permanent human residents.
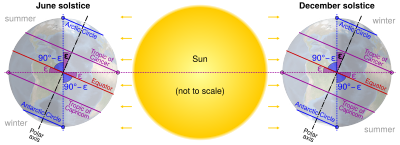
If Earth had no atmosphere, you would see days inside these circles where the sun never sets (a polar day). You would also see days where the sun never rises (a polar night). Near the North Pole and South Pole, these periods can last for half the year! However, Earth does have an atmosphere. This, along with the sun's size, means the exact boundaries for polar day and night are a little different from the circles themselves.
What Are Polar Circles?
The position of the polar circles depends on Earth's 'axial tilt'. This is the tilt of Earth's axis as it spins, compared to its orbit around the sun. Earth's axis is tilted about 23.5 degrees. This tilt is what causes our seasons.
The latitude of the polar circles is calculated by subtracting Earth's axial tilt from 90 degrees. For example, 90 degrees minus about 23.5 degrees equals roughly 66.5 degrees. This is why the polar circles are found at approximately 66.5 degrees North and South. Earth's tilt changes very slightly over time. This small change means the exact position of the polar circles also shifts a little each year.
Polar Day and Polar Night
Inside the polar circles, you can experience amazing natural events: the polar day and the polar night. These happen because of Earth's tilt.
During a polar day, the sun stays visible for more than 24 hours. It might even stay up for weeks or months near the poles! This is also known as the "midnight sun." During a polar night, the sun does not rise for more than 24 hours. It can be dark for weeks or months.
Why the Boundaries Aren't Exact
The polar circles almost perfectly match the areas where polar day and polar night occur. However, there are two main reasons why the observed boundaries are slightly different:
- Atmospheric Refraction: Earth's atmosphere bends sunlight. This makes the sun appear higher in the sky than it actually is. So, you might see the sun even when it is technically below the horizon.
- Sun's Angular Diameter: The sun isn't a tiny point of light. It's a big circle! So, even when its center is below the horizon, part of it might still be visible.
These two factors mean that the actual areas of polar day and polar night are slightly different from the exact lines of the polar circles. The observed boundaries can be about 80 to 100 kilometers away from the circle lines. Also, Earth's tilt has a very tiny wobble called 'nutation'. This causes very small, additional changes in the circles' positions. If you are higher above sea level, you might also see the sun a little earlier or later.
See also
 In Spanish: Círculo polar para niños
In Spanish: Círculo polar para niños
- Antarctica
- Antarctic Circle
- Arctic
- Arctic Circle
- Frigid zones
- Polar climate
- Polar day and Polar night
- Polar region
 | Georgia Louise Harris Brown |
 | Julian Abele |
 | Norma Merrick Sklarek |
 | William Sidney Pittman |