Reticular fiber facts for kids
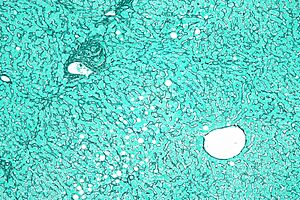
Reticular fibers, also called reticulin, are a special kind of tiny fiber found in your body's connective tissue. Think of them like a super-fine, delicate net or mesh that helps support many soft organs and tissues. They are made from a specific type of protein called type III collagen.
These fibers are secreted by special cells called reticular cells. Once secreted, they link together to form a fine network. This network acts as a supportive framework, especially in organs like the liver, bone marrow, and parts of your lymphatic system, which is important for your immune system.
Contents
What Are Reticular Fibers?
Reticular fibers are very thin and delicate threads that form a supportive web inside your body. They are a key part of connective tissue, which is like the "glue" that holds your body together and gives it shape. Unlike thicker collagen fibers, reticular fibers are much finer and branch out a lot, creating a flexible, mesh-like structure.
Building Blocks: Type III Collagen
The main ingredient of reticular fibers is a protein called type III collagen. Collagen is the most common protein in your body, and it's super strong. While many types of collagen exist, type III is special because it forms these very thin, branching fibers. These fibers are made by cells called fibroblasts, but in some places, specialized cells called reticular cells produce them.
Where Do We Find Them?
Reticular fibers are found in many places where a delicate but strong support system is needed. They are like the scaffolding that holds cells in place in soft, spongy organs.
Supporting Your Organs
You can find a lot of reticular fibers in your liver. They form a fine network that supports the liver cells, helping them stay organized. They are also important in your spleen and lymph nodes, which are key parts of your immune system. In these organs, the reticular network provides a framework for immune cells to move around and do their job.
Helping Blood and Immune Cells
Reticular fibers are also very important in your bone marrow. This is where your body makes new blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. The reticular network in the bone marrow acts like a soft bed, supporting the developing blood cells and helping them mature properly.
In Your Skin and More
While less common than other collagen types, reticular fibers are also present in your skin. They contribute to the skin's flexibility and strength. You can also find them around small blood vessels, nerves, and in some endocrine glands, providing essential support to these delicate structures.
How Are They Different?
Your body has different types of fibers in its connective tissue.
- Collagen fibers (like type I) are thick, strong, and don't stretch much. They are found in tendons and ligaments.
- Elastic fibers are stretchy and can snap back into shape, like a rubber band. They are found in your skin and blood vessels.
- Reticular fibers are unique because they are very thin, branch out widely, and form a delicate, supportive mesh. They are not as strong as thick collagen fibers, but their branching structure is perfect for holding cells in place in soft tissues.
Why Are They Important?
Reticular fibers play a vital role in maintaining the structure and function of many organs. Without their delicate support network, cells in organs like the liver or bone marrow wouldn't have a proper framework to grow and work effectively. They are essential for filtering blood, producing blood cells, and supporting your immune system.
See also
 In Spanish: Fibra reticular para niños
In Spanish: Fibra reticular para niños