Ribosome facts for kids
Ribosomes are super important parts of every living cell. Think of them as tiny machines inside your cells! Each ribosome is made up of two main things: RNA (a type of genetic material) and protein.
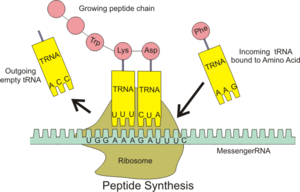
Their main job is to create proteins. They do this by reading instructions from a special molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA). This process is called translation. Ribosomes take small building blocks called amino acids and link them together in a specific order to form a protein.
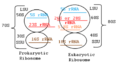
Ribosomes are found in all living cells, whether they are simple cells like bacteria (prokaryotes) or more complex cells like those in plants and animals (eukaryotes).
Ribosomes start to form in a special area of the cell's nucleus called the nucleolus. The nucleus is like the cell's control center, and it's protected by a barrier called the nuclear envelope. This envelope has tiny holes, or pores, that let things move in and out.
Once formed, ribosomes get to work making new proteins. They move along the mRNA strand, reading its code and adding amino acids one by one. Many ribosomes are found attached to a network inside the cell called the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Others float freely in the cytoplasm, which is the jelly-like substance that fills the cell.
How Ribosomes Are Built
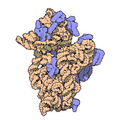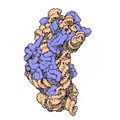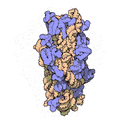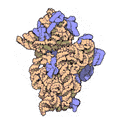
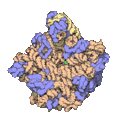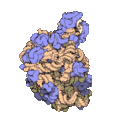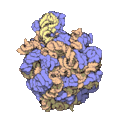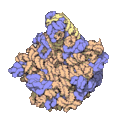
Every ribosome has two main pieces, called subunits. Imagine them like two puzzle pieces that fit together!
- The small subunit is like the reader. It grabs onto the messenger RNA and reads the instructions.
- The large subunit is like the builder. It connects the amino acids together to form a long chain, which becomes a protein.
Both of these subunits are made of different kinds of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules and many different proteins. These parts work together perfectly to make sure the right proteins are built for the cell to function.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Ribosoma para niños
In Spanish: Ribosoma para niños
 | Sharif Bey |
 | Hale Woodruff |
 | Richmond Barthé |
 | Purvis Young |