STS-54 facts for kids

Endeavour deploys the TDRS-F satellite.
|
|
| Names | Space Transportation System-54 |
|---|---|
| Mission type | TDRS-F satellite deployment Technology research |
| Operator | NASA |
| Mission duration | 5 days, 23 hours, 38 minutes, 17 seconds |
| Distance travelled | 2,501,277 mi (4,025,415 km) |
| Orbits completed | 96 |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft | Space Shuttle Endeavour |
| Landing mass | 92,988 kg (205,003 lb) |
| Payload mass | 18,559 kg (40,916 lb) |
| Crew | |
| Crew size | 5 |
| Members |
|
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | January 13, 1993, 13:59:30 UTC (8:59:30 am EST) |
| Launch site | Kennedy, LC-39B |
| Contractor | Rockwell International |
| End of mission | |
| Landing date | January 19, 1993, 13:37:47 UTC (8:37:47 am EST) |
| Landing site | Kennedy, SLF Runway 33 |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric orbit |
| Regime | Low Earth orbit |
| Perigee | 302 km (188 mi) |
| Apogee | 309 km (192 mi) |
| Inclination | 28.45 degrees |
| Period | 90.60 minutes |
 STS-54 mission patch  From left: Runco, Casper, McMonagle, Helms and Harbaugh |
|
STS-54 was an exciting NASA space mission that took place in January 1993. It used the Space Shuttle Endeavour, one of the amazing vehicles from the Space Shuttle program. This was the third time Endeavour flew into space. The main goal of STS-54 was to launch a special satellite and conduct several science experiments. The mission also included a spacewalk to help astronauts prepare for future work in space.
Contents
Discovering Space with STS-54
Meet the Astronaut Crew
A team of five brave astronauts flew aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour for the STS-54 mission. They were:
| Position | Astronaut | |
|---|---|---|
| Commander | John Casper Second spaceflight |
|
| Pilot | Donald R. McMonagle Second spaceflight |
|
| Mission Specialist 1 | Mario Runco Jr. Second spaceflight |
|
| Mission Specialist 2 Flight Engineer |
Gregory J. Harbaugh Second spaceflight |
|
| Mission Specialist 3 | Susan Helms First spaceflight |
|
Where Did Everyone Sit?
The astronauts had specific seats for launch and landing. Most of them had flown before, but Susan Helms was on her very first space mission!
| Seat | Launch | Landing | 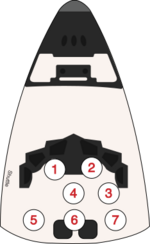 Seats 1–4 were on the flight deck. Seats 5–7 were on the mid-deck. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Casper | ||
| 2 | McMonagle | ||
| 3 | Runco | Helms | |
| 4 | Harbaugh | ||
| 5 | Helms | Runco | |
| 6 | Unused | ||
| 7 | Unused | ||
Exciting Mission Goals
The STS-54 mission had several important tasks to complete during its six days in space.
Launching a Special Satellite
The main job for STS-54 was to deploy the fifth TDRS satellite, called TDRS-F. TDRS stands for Tracking and Data Relay Satellite. These satellites act like giant relay stations in space. They help NASA communicate with other spacecraft, like the Space Shuttle itself or the International Space Station, when they are out of direct sight from ground stations. After being released from Endeavour, a special rocket stage called the Inertial Upper Stage (IUS) pushed TDRS-F into its correct orbit high above Earth.
The shuttle also carried a special experiment called the Diffuse X-ray Spectrometer (DXS). This instrument looked for X-ray radiation coming from distant parts of space. It helped scientists learn more about the universe.
Science Experiments in Space
Astronauts also conducted several experiments inside the shuttle's middeck. These experiments studied how things behave in microgravity, which is the feeling of weightlessness in space.
- Commercial General Bioprocessing Apparatus (CGPA): This experiment was for life sciences research. It helped scientists understand how biological processes work without Earth's gravity.
- Chromosome and Plant Cell Division in Space Experiment (CHROMEX): This experiment studied how plants grow and how their cells divide in space. It helped us learn if plants could grow normally on long space missions.
- Physiological and Anatomical Rodent Experiment (PARE): Scientists used this experiment to study how the skeletal system and bones of small animals adapt to spaceflight. This research is important for understanding how human bones might change in space.
- Space Acceleration Measurement Equipment (SAMS): This device measured tiny changes in the feeling of weightlessness inside the shuttle. This data was important for other experiments that needed a very stable, microgravity environment.
- Solid Surface Combustion Experiment (SSCE): This experiment looked at how flames spread and how hot burning materials get in space. Understanding fire in space is crucial for astronaut safety.
Astronauts Take a Spacewalk!
On the fifth day of the mission, two mission specialists, Mario Runco Jr. and Gregory J. Harbaugh, went outside the shuttle for a spacewalk! They spent almost five hours floating in the open cargo bay. This spacewalk was a special addition to the mission.
The main goal of their spacewalk was to practice and learn more about working in space. They tested how easily they could move around the cargo bay and how to use foot restraints without using their hands. They even pretended to carry large objects in the weightless environment. This practice was very important for NASA. It helped them prepare for building the International Space Station, which would require many spacewalks to assemble different parts.
The spacewalk lasted for 4 hours and 28 minutes. After a successful mission, Endeavour landed back at the Kennedy Space Center on January 19, 1993.
Learn More About Space
- List of human spaceflights
- List of Space Shuttle missions
- Outline of space science
- Space Shuttle


