Rice white stemborer facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Scirpophaga innotata |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Subphylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Superfamily: |
Pyraloidea
|
| (unranked): |
Obtectomera
|
| Family: | |
| Subfamily: |
Schoenobiinae
|
| Genus: |
Scirpophaga
|
| Species: |
S. innotata
|
| Binomial name | |
| Scirpophaga innotata (Walker, 1863)
|
|
| Synonyms | |
|
|
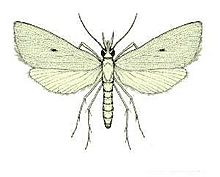
The Rice White Stemborer (Scirpophaga innotata) is a type of moth that can be a big problem for rice plants. It's known for its white color and for boring into the stems of rice plants, which can damage the crop. This moth is found in warm, tropical parts of the world, like Indonesia, Pakistan, the Philippines, and northern Australia.
Contents
About the Rice White Stemborer
The Rice White Stemborer is a small insect. It belongs to a group of moths called Crambidae. These moths are often found near water or in grassy areas.
What is a Moth?
A moth is an insect that is related to a butterfly. Moths usually fly at night. They have wings covered in tiny scales. Moths go through a full metamorphosis during their life. This means they change completely from a larva (caterpillar) to a pupa, and then to an adult moth.
Where Does It Live?
This moth prefers warm, tropical places. You can find it in countries like Indonesia, Pakistan, and the Philippines. It also lives in the tropical northern parts of Australia. These areas are perfect for growing rice, which is the moth's main food source.
What Does It Look Like?
The adult Rice White Stemborer is mostly white. It is a small moth, usually only a few centimeters long. Its wings are narrow and have a silky look. The larvae, or caterpillars, are also pale. They are the stage of the moth that causes damage to rice plants.
Life Cycle of the Rice White Stemborer
Like all moths, the Rice White Stemborer goes through four main stages in its life. These stages are egg, larva, pupa, and adult. This process is called a complete life cycle.
Eggs
The adult female moth lays her tiny eggs on the leaves of rice plants. She often covers them with a protective layer of hairs. This helps to hide them from predators. The eggs are usually laid in groups or clusters.
Larvae (Caterpillars)
After a few days, the eggs hatch into small larvae. These larvae are also known as caterpillars. The caterpillars are the most damaging stage of the moth. They bore into the stems of rice plants. Inside the stem, they eat the plant from the inside out. This makes the plant weak and can stop it from growing properly.
Pupae
Once the larva has grown enough, it changes into a pupa. The pupa stage is a resting stage. During this time, the larva transforms into an adult moth. The pupa is often found inside the rice stem or in the soil near the plant.
Adult Moths
Finally, the adult moth emerges from the pupa. These adult moths are white and can fly. Their main job is to find a mate and lay eggs. This starts the whole life cycle over again. Adult moths do not eat the rice plants. They might feed on nectar from flowers.
Why is it Important?
The Rice White Stemborer is a well-known pest in rice-growing regions. It can cause significant damage to rice crops. This can affect the food supply for many people.
Damage to Rice Plants
When the larvae bore into the rice stems, they cut off the plant's food and water supply. This causes the central part of the plant to wilt and die. This damage is often called "deadheart" because the center of the plant turns white and dies. If the damage happens later, when the plant is older, it can cause "whiteheads." This means the rice grains do not form properly and the heads of the plant turn white and empty. Farmers use different methods to control these moths. This helps to protect their valuable rice crops.

