Serous membrane facts for kids
A serous membrane (also called serosa) is a special kind of smooth tissue found inside your body. Think of it like a very thin, slippery sheet that covers and protects your organs.
This membrane is made of two layers of special cells. One layer, called the visceral membrane, sits directly on top of your organs, like a glove. The other layer, called the parietal layer, lines the walls of the body cavities where these organs are located.
Between these two layers is a tiny space, almost empty, but it contains a small amount of lubricating fluid called serous fluid. This fluid is secreted by the membrane itself. Its main job is to reduce friction, helping your organs move smoothly against each other and against the body wall when you breathe, digest food, or move around. Without this fluid, organs rubbing together could cause damage.
Serous membranes are found in several important places in your body:
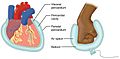
- The membrane around your heart is called the pericardium.
- The membrane lining your chest cavity and surrounding your lungs is called the pleura.
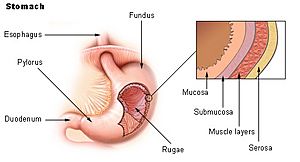
- The membrane lining your belly area (abdomen) and covering your digestive organs is called the peritoneum.
It's important to know that serosa is different from another type of tissue called adventitia. While serosa is smooth and helps things slide easily, adventitia is a tougher connective tissue that helps bind structures together.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Serosa para niños
In Spanish: Serosa para niños
 | Shirley Ann Jackson |
 | Garett Morgan |
 | J. Ernest Wilkins Jr. |
 | Elijah McCoy |