Plug-in (computing) facts for kids
A plug-in (or add-on) is like a small piece of software. It adds new features to a main program. Think of it as an extra tool you can attach to a bigger tool. This lets the main program do more things. It also means the main program doesn't need to be completely changed.
Programs use plug-ins for several good reasons:
- They let other software makers add new features.
- It's easy to add new tools without changing the main program.
- The main program can be smaller. It only loads features when you need them.
- It helps keep different parts of the software separate.
Contents
What Are Some Examples of Plug-ins?
Plug-ins are used in many different types of software. Here are some common examples:
Audio and Music Programs
Programs for making or editing music use audio plug-ins. These plug-ins can create sounds. They can also change how sounds are processed or analyzed. Examples of such programs include Ardour, Audacity, Cubase, and FL Studio.
Email Programs
Email programs use plug-ins to help keep your messages private. For example, some plug-ins can encrypt or decrypt emails. This means they can scramble and unscramble your messages. Pretty Good Privacy is one such plug-in.
Video Game Emulators
Video game console emulators are programs that let you play old games. They often use plug-ins for different parts of the game console. For instance, the PCSX2 emulator uses plug-ins for video, audio, and disc reading. These plug-ins help it act like a PlayStation 2.
Graphics and Photo Software
Programs for editing photos or creating graphics use plug-ins. These plug-ins help them open different file types. They also help process images. A Photoshop plug-in is a good example of this.
Broadcasting and Live-Streaming Software
Software like OBS Studio uses plug-ins. These plug-ins help users add special features. They can customize their live streams or broadcasts.
Media Players
Media players use plug-ins to play different types of media files. They can also apply special effects to videos or music. foobar2000 and Winamp are examples of media players that use plug-ins.
Text Editors and Programming Tools
Programs for writing text or computer code use plug-ins. These plug-ins help them understand different programming languages. They also make it easier to write code. Programs like Visual Studio and Eclipse use plug-ins.
Web Browsers (Older Use)
Web browsers used to use plug-ins a lot. These plug-ins helped them show special content. Examples included Adobe Flash Player for animations or Java virtual machine for interactive apps. Most of these browser plug-ins are not used anymore. However, Browser extensions are still very common. They are a different type of add-on.
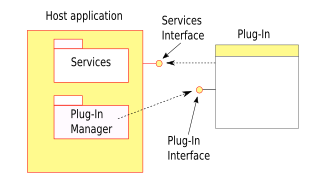
How Do Plug-ins Work?
The main program provides services that plug-ins can use. It also has a way for plug-ins to connect to it. Plug-ins need the main program to work. They usually cannot run by themselves.
On the other hand, the main program works fine without the plug-ins. This means you can add or update plug-ins easily. You don't need to change the main program itself.
Programmers often create plug-ins as shared libraries. These are like small code packages. The main program loads them when it needs them. This happens while the program is running. Sometimes, programs also use simple script files as plug-ins. These scripts are written in languages like Python.
What is a Helper Application?
A helper application is a separate program. It works with a web browser. Examples include IrfanView for images or Adobe Reader for PDF files. A helper application adds features to a browser. But unlike a plug-in, it runs as its own program. It does not run inside the browser's memory. This means if the helper application crashes, it won't crash the browser.
A Brief History of Plug-ins
The idea of plug-ins has been around for a while. In the mid-1970s, a text editor called EDT allowed other programs to run from it. These programs could change the text being edited.
Early personal computer software also used plug-ins. HyperCard and QuarkXPress on the Apple Macintosh had this ability. Both were released in 1987. In 1988, Silicon Beach Software added plug-in features to its programs Digital Darkroom and SuperPaint.
See also
 In Spanish: Complemento (informática) para niños
In Spanish: Complemento (informática) para niños
- Add-on (Mozilla)
- Applet
- Browser extension
- Theme
 | Chris Smalls |
 | Fred Hampton |
 | Ralph Abernathy |