Boa dragonfish facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Boa dragonfish |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Preserved Specimen | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Genus: |
Stomias
|
| Species: |
boa
|
| Synonyms | |
|
|
The Stomias boa, also known as the boa dragonfish or scaly dragonfish, is a fascinating deep-sea fish. It belongs to a family of fish called Stomiidae, which are known for living in the ocean's dark depths.
Scientists used to think there were different types (called subspecies) of Stomias boa. But now, after more study, they have decided that these types are actually separate species of dragonfish. For example, what was once called Stomias boa ferox is now known as Stomias ferox. This helps scientists understand these amazing creatures better.
Contents
What Does the Boa Dragonfish Look Like?
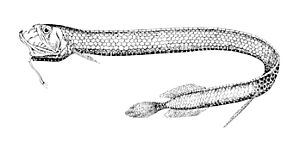
The Stomias boa has a long, thin body. It can grow up to about 32.2 centimeters (about 1 foot) long. Its belly is black, and its sides are a shiny, iridescent silver, which means they shimmer with different colors.
Special Features
This fish has a small head and a unique feature called a barbel. This is a long, thin growth that hangs from its chin. The barbel has a pale stem, a dark spot near its base, and three dark, thin threads.
One of the coolest things about the Stomias boa is its ability to make light. It has six rows of special hexagonal (six-sided) areas on its skin. Below these areas are large photophores. Photophores are like tiny light-producing organs that help the fish see in the dark ocean or attract prey.
Its dorsal fin (top fin) and anal fin (bottom fin) are located opposite each other. They are found just before its caudal fin (tail fin).
Where Does the Boa Dragonfish Live?
The Stomias boa is a deep-sea creature. It lives in the mesopelagic and bathypelagic zones of the ocean. This means it can be found at depths from about 200 meters (656 feet) down to 2,173 meters (7,129 feet). That's super deep!
You can find this fish in oceans all over the world. It's especially common off the Atlantic coast of North America and in the Mediterranean Sea. It also lives in a wide band across the southern oceans, between 20° and 45° South latitude.
What Does the Boa Dragonfish Eat?
The Stomias boa is a predator in the deep sea. It eats other fish that live in the middle layers of the ocean. It also enjoys eating crustaceans, which are creatures like shrimp and crabs.
To find food, the Stomias boa often rises closer to the surface of the ocean at night. This is when many smaller creatures also move upwards, making it easier for the dragonfish to hunt.
How Does the Boa Dragonfish Reproduce?
The Stomias boa reproduces by laying eggs. This is called being oviparous. When the eggs hatch, the baby fish are called larvae. These larvae are quite small, ranging from about 9 to 44 millimeters (0.35 to 1.7 inches) in length.