Subdural hematoma facts for kids
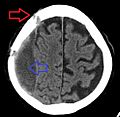
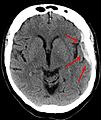
A subdural hematoma (say "sub-DOOR-al HEM-uh-TOE-muh"), often called an SDH, is when blood collects in a specific spot around your brain. This usually happens after a head injury, like a hard bump or fall. The blood gathers between two of the protective layers that cover your brain.
These layers are called the dura mater and the arachnoid mater. They are part of the meninges, which are like a set of protective blankets around your brain. A subdural hematoma happens when tiny blood vessels, called bridging veins, tear in this space.
Because these are veins, not arteries, the bleeding is usually slower. This means that the signs and symptoms of a subdural hematoma might not show up right away. They could appear within minutes or hours, but sometimes it can take up to two weeks for them to become noticeable.
Contents
What is a Subdural Hematoma?
Your brain is protected by your skull and three layers of tissue called the meninges. Think of these layers as special coverings. A subdural hematoma is a pool of blood that forms between two of these layers: the dura mater (the tough outer layer) and the arachnoid mater (the middle layer).
This collection of blood can press on the brain. If it gets too big, it can cause serious problems because the brain has less space inside the skull.
How Does It Happen?
Most subdural hematomas are caused by a traumatic brain injury. This means an injury that causes a sudden jolt or hit to the head. For example, it could be from:
- A fall
- A car accident
- A sports injury
When your head gets a hard bump, the brain can move inside the skull. This movement can stretch and tear the small "bridging veins" that connect the brain's surface to the dura mater. When these veins tear, blood leaks out and starts to collect in the subdural space.
What Are the Signs?
The signs of a subdural hematoma can be different for everyone and depend on how much blood has collected. Because veins bleed slowly, the symptoms might not show up immediately after the injury. They can develop over hours, days, or even weeks.
Some common signs to watch out for after a head injury include:
- A bad headache that doesn't go away
- Feeling confused or dizzy
- Trouble speaking or understanding
- Weakness or numbness on one side of the body
- Changes in vision
- Feeling very sleepy or losing consciousness
- Vomiting
If someone has a head injury and then shows any of these signs, it's important to get medical help right away.
Images for kids
-
Micrograph of a chronic subdural hematoma, as demonstrated by thin strands of collagen and neovascularization. HPS stain
See also
 In Spanish: Hematoma subdural para niños
In Spanish: Hematoma subdural para niños