Sun angle facts for kids
The sun angle is simply how high or low the Sun appears in the sky. It also describes how directly the Sun's light hits the Earth's surface at a specific time and place. Imagine a flashlight: if you shine it straight down, the light is bright and focused. If you shine it at a slant, the light spreads out and isn't as strong. Sunlight works in a similar way.
In most places, the Sun rises in the morning, reaches its highest point around noon, and then sets in the evening. As the Sun moves across the sky, its angle changes. This angle is really important because it controls how much heat energy a place receives. This is why summer days are usually much warmer than winter days!
Contents
Why the Sun Angle Changes
The main reason the sun angle changes throughout the year is because of the Earth's tilt. Our planet doesn't spin straight up and down. Instead, its axis is tilted about 23.5 degrees. As the Earth travels around the Sun, different parts of the planet are tilted towards or away from the Sun.
Daily Changes in Sun Angle
Every day, the sun angle changes from sunrise to sunset.
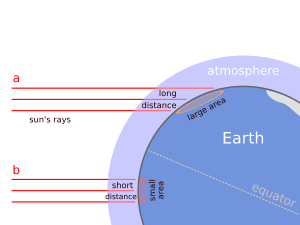
- At sunrise and sunset, the Sun is low in the sky. Its rays hit the Earth at a very shallow angle. This means the sunlight is spread out over a larger area. That's why it feels cooler in the mornings and evenings.
- Around noon, the Sun is at its highest point. Its rays hit the Earth more directly. This concentrates the sunlight into a smaller area, making it feel warmer.
Seasonal Changes in Sun Angle
The tilt of the Earth's axis causes the biggest changes in sun angle, leading to our seasons.
- When your part of the Earth is tilted towards the Sun, the sun angle is higher. The sunlight hits more directly, bringing warmer temperatures and longer days. This is summer!
- When your part of the Earth is tilted away from the Sun, the sun angle is lower. The sunlight hits at a shallower angle, spreading out the heat. This results in cooler temperatures and shorter days. This is winter!
Sun Angle at the Poles
The sun angle has a huge effect on the polar regions.
- Near the North Pole and South Pole, the sun angle is always very low, even in their summer. This means the sunlight is always spread out. That's why these areas are so cold, even when they have 24 hours of daylight!
- During their winter, the poles are tilted completely away from the Sun. The sun angle becomes so low that the Sun doesn't even rise for months, leading to long periods of darkness.
How Sun Angle Affects Life
The sun angle is a basic mechanism that affects many things on Earth.
- Temperature: It directly controls how warm or cold a place is.
- Day Length: A higher sun angle usually means longer days, while a lower angle means shorter days.
- Plant Growth: Plants need sunlight to grow. The amount and intensity of sunlight (affected by sun angle) impact farming and natural ecosystems.
- Solar Power: The efficiency of solar panels depends on the sun angle. Panels work best when the sun's rays hit them directly.
Related pages
 | Jackie Robinson |
 | Jack Johnson |
 | Althea Gibson |
 | Arthur Ashe |
 | Muhammad Ali |